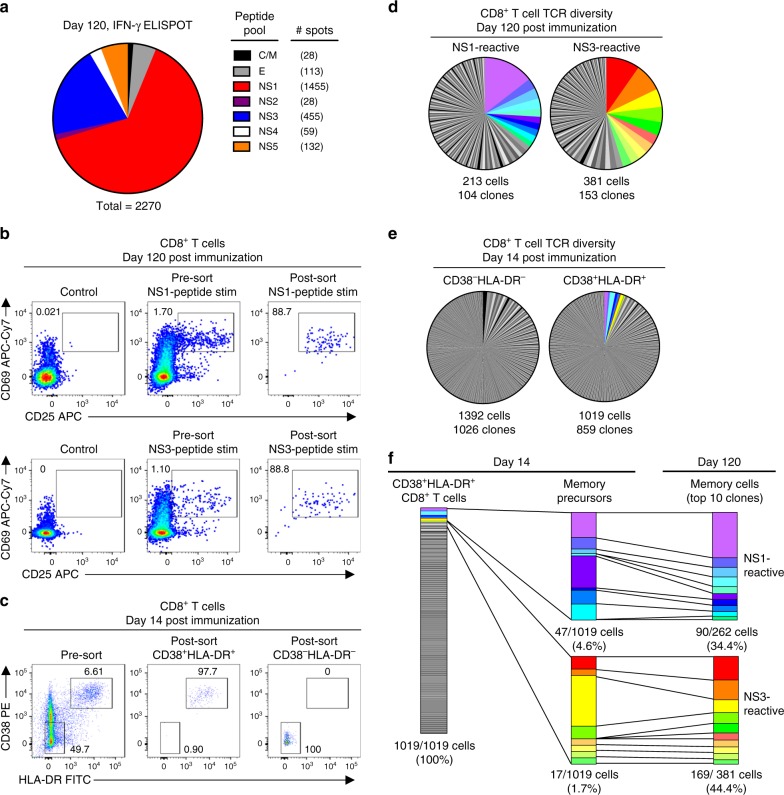
Fig. 2.
TAK-003-elicited CD38+ HLA-DR+ CD8+ T cells are highly polyclonal and persist as long-lived memory cells. TCR clonotype diversity was assessed within acutely-activated and DENV-reactive memory CD8+ T cells using single-cell RNA sequencing. a The antigenic specificity of DENV-reactive memory CD8+ T cells from a TAK-003 recipient was assessed by IFN-γ ELISPOT 120 days post immunization. The number of spots is presented relative to 1 million PBMCs. b NS1-reactive and NS3-reactive memory CD8+ T cells from 120 post-vaccination were isolated by flow cytometry based on upregulation of CD25 and CD69 expression following in vitro stimulation for 18 h with 1 μg ml−1 of the indicated peptide pools. c Activated (CD38+ HLA-DR+) CD8+ T cells and non-activated (CD38−HLA-DR−) CD8+ T cells were additionally isolated by flow cytometry from the same TAK-003 recipient 14 day post-vaccination. d TCR clonotype diversity from sorted NS1-reactive and NS3-reactive CD8 + T cells isolated 120 days post-vaccination. The top 10 most abundant NS1- and NS3-reactive clones are demarcated in color. e TCR clonotype diversity in sorted non-activated (CD38−HLA-DR−) and activated (CD38+ HLA-DR+) CD8+ T cells using scRNAseq from 14 days post-TAK-003 administration. TCR clones that overlap with the dominant NS1- or NS3-reactive memory CD8+ T cell clones observed at day 120 are indicated with the appropriate color designation. f Assessment of the relative contribution and stability of the dominant NS1- and NS3-reactive memory precursors to the overall CD38+HLA-DR+ CD8+ T cell pool at day 14 post-TAK-003 immunization