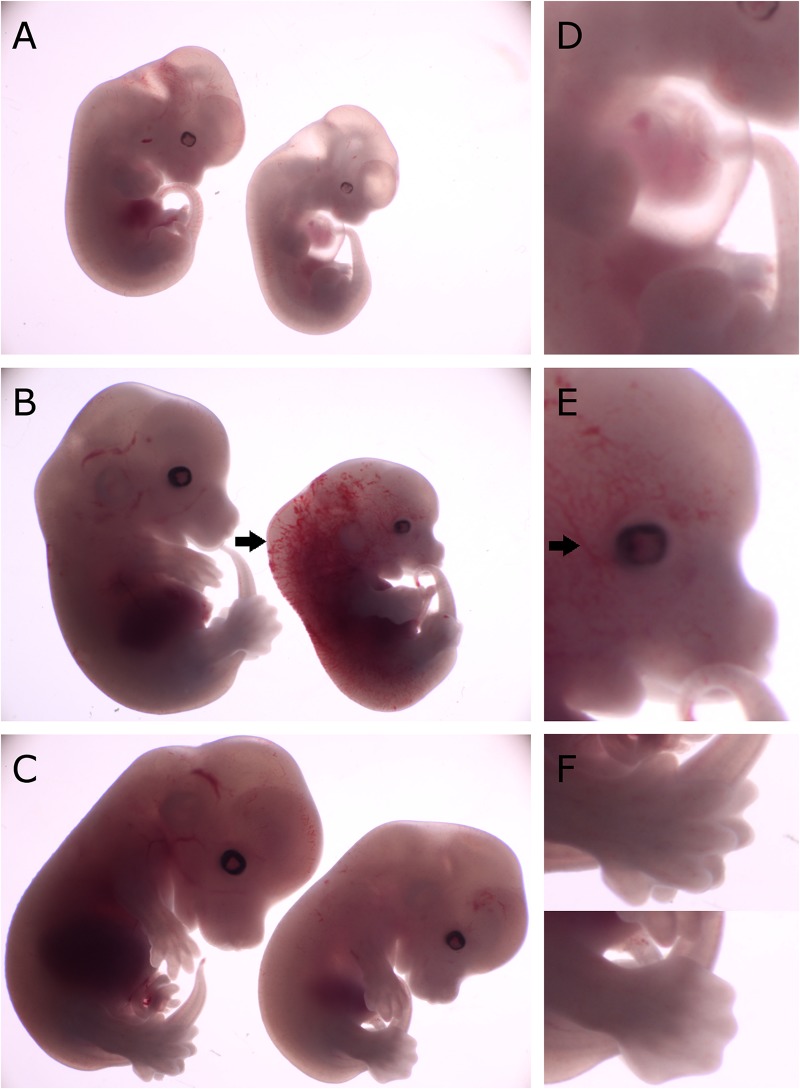
FIGURE 2.
Comparison of gross morphology of wild-type, Cdk13tm1a/+ and Cdk13tm1a/tm1a embryos at various stages. Cdk13tm1a/tm1a embryos display significant growth retardation compared to wild-type and heterozygous embryos. (D–F) Detailed images of Cdk13tm1a/tm1a at relevant developmental stages. (A) Heterozygous and Cdk13tm1a/tm1a embryos at E12.5. (D) Occasional chest wall deformities manifest at hypomorphs. (B) Wild-type and Cdk13tm1a/tm1a embryos at E13.5. Cdk13tm1a/tm1a embryo exhibits nuchal edema (black arrow). (E) Hypervascularization of the peripheral vessels capillaries (black arrow). (C) Wild-type and Cdk13tm1a/tm1a embryos at E14.5. (F, top) Wild-type embryo demonstrates deep indentations between the developing fingers of embryos E14.5, although not yet separated. (F, bottom) In contrast, Cdk13tm1a/tm1a embryo appears to be 1 day delayed in development as evidenced by the shallow indentation of the footpad, which is characteristic of embryos E13.5.