Figure 5. A conserved sRNA motif is enriched in laboratory selection experiments.
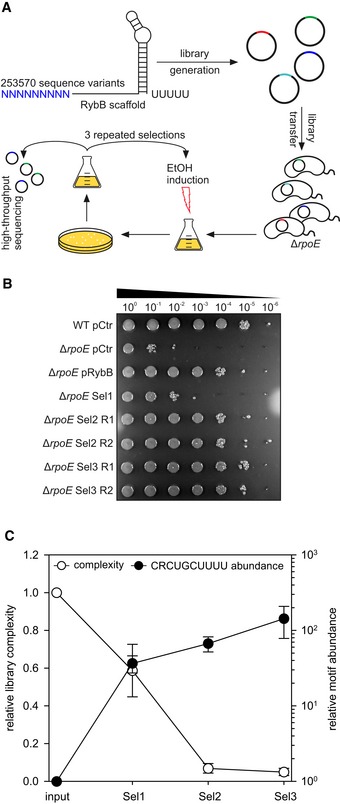
- Experimental strategy of the laboratory selection experiments: An sRNA library was generated using the rybB scaffold with nine randomized nucleotides at the 5′ end, cloned into a broad‐range plasmid backbone, and transferred into V. cholerae ΔrpoE cells. These colonies were pooled, grown to OD600 of 0.2, and treated with ethanol (3.5% final conc.) for 6 h. Surviving cells were recovered on agar plates, pooled, and subjected to another round of selection (3 selections total). After each selection, the plasmids of surviving cells were analyzed using high‐throughput sequencing.
- Vibrio cholerae wild‐type and ΔrpoE strains carrying an empty vector control (pCtr), pRybB, or the sRNA library after consecutive selection experiments (Sel1, Sel2, and Sel3) were grown in LB medium to OD600 of 0.2. Cells were treated with ethanol (3.5% final conc.) for 6 h. Serial dilutions were prepared and spotted onto agar plates. R1 and R2 indicate two independent biological replicates.
- Plasmid contents of the strains carrying the sRNA libraries before selection (input) and after consecutive ethanol treatments (Sel1, Sel2, and Sel3) were analyzed using high‐throughput sequencing. Relative library complexity (left y‐axis) was determined by counting sequence variants present in the normalized samples. To test for the enrichment of possible sequence motifs, the sequence variants present in each sample were counted and normalized for sequencing depth. The resulting data were analyzed for the enrichment of the conserved CRCUGCUUUU motif (right y‐axis).
