-
A
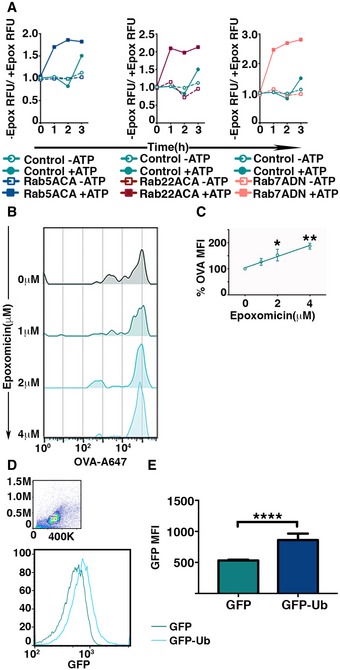
Activity of proteasomes within the phagosomes was determined by measuring the fluorescence intensity of fluorogenic proteasome substrate incubated with latex beads from detergent‐treated phagosomes treated or untreated with epoxomicin. The fluorescence intensities were measured at 1‐h intervals, and values plotted represent the ratio of the signals in the absence versus the presence of epoxomicin (A).
-
B, C
Intraluminal proteasome‐dependent degradation of phagocytosed antigen was measured by flow cytometric analysis of phagocytosed latex beads covalently conjugated with Alexa 647‐OVA. Latex beads were extracted by mechanical disruption of BMDC and incubated with ATP, lysosomal protease inhibitor cocktail, and varying dose of epoxomicin at 37°C for 16 h. After incubation, latex beads were treated with detergent and analyzed by flow cytometry (B). The mean of Alexa 647 fluorescence associated with the latex beads incubated with epoxomicin was normalized to fluorescence of untreated beads from independent experiments were plotted (n = 4) (C).
-
D, E
Ubiquitination of phagosomal cargo within the phagosomes was assessed by measuring the acquisition of GFP fluorescence by phagocytosed latex beads conjugated with OVA post‐detergent extraction from BMDC expressing GFP or GFP‐Ub (D). The mean of fluorescence intensities of GFP on the beads from independent experiments was plotted (E).
Data information: In (A), representative experiments of three independent experiments are shown for each Rab mutant. In (C), the means (±SEM) are plotted. Data obtained from five independent experiments were analyzed by performing a linear regression analysis, and **
P < 0.01, *
P < 0.05 (one‐way ANOVA). In (E), the mean ± SEM of six independent experiments has been plotted. ****
P < 0.001 (Student's
t‐test).