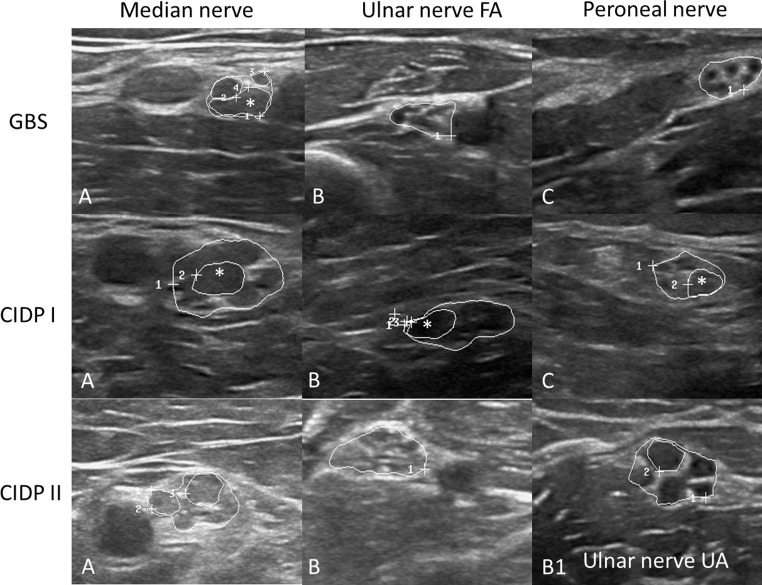
Fig. 3.
Examples of median (A), ulnar (B), and fibular/peroneal nerves (C) in one GBS (first row) and two CIDP patients. In the GBS patient, the echointensity of the fascicles is hypo- to isoechoic, only the median nerve (MN) is slightly enlarged—only in the upper arm—regionally restricted (13 mm2, cut-off 12 mm2), whereas ulnar and fibular nerves (UN and FN) are not enlarged. Only one fascicle is enlarged (*, MN, CSA 7 mm2, cut-off, 4.8 mm2, 15). In the CIDP I patient in contrast, all nerves are enlarged to a different amount (MN 45 mm2, the UN 26 mm2, cut-off 8.5 mm2 and the FN 18 mm2, cut-off 11.5 mm2). In all nerves, at least one fascicle is enlarged (* 10 mm2 in the MN, 6 and 7 mm2 in UN and FN, cut-off 2.8 and 3.5 mm2). In CIDP II, the MN is enlarged with 25 mm2 and reveals increased echointensity, and the UN is enlarged at two sites—homogeneously (18 mm2 in the upper arm (B1) with reduced echo signal and 13 mm2 in the forearm with increased echo signal (B)). Nerves are surrounded by white circles; the mentioned fascicles are marked with asterisk symbols