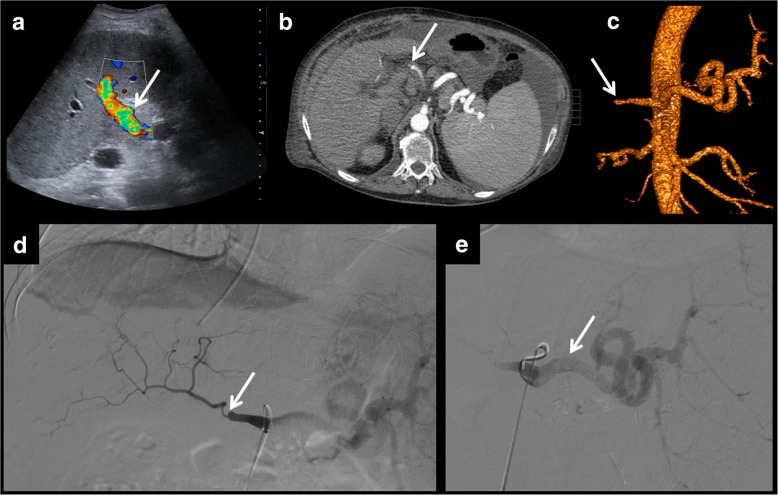
Fig. 6.
Hepatic artery stenosis leading to splenic artery steal syndrome. Postsurgical US shows a turbulent flow of the hepatic vein. The hepatic artery cannot be clearly identified (a). An arterial phase CT is performed, showing severe focal stenosis of the hepatic artery and filiform enhancement of its branches (b, c). The increased size of the splenic artery should also be noted. Increased splenic artery blood flow explains the increased turbulent portal flow. Angiography confirms both stenosis of the hepatic artery and the increased size of the splenic artery (d, e). Distal embolisation of the splenic artery was performed as a treatment