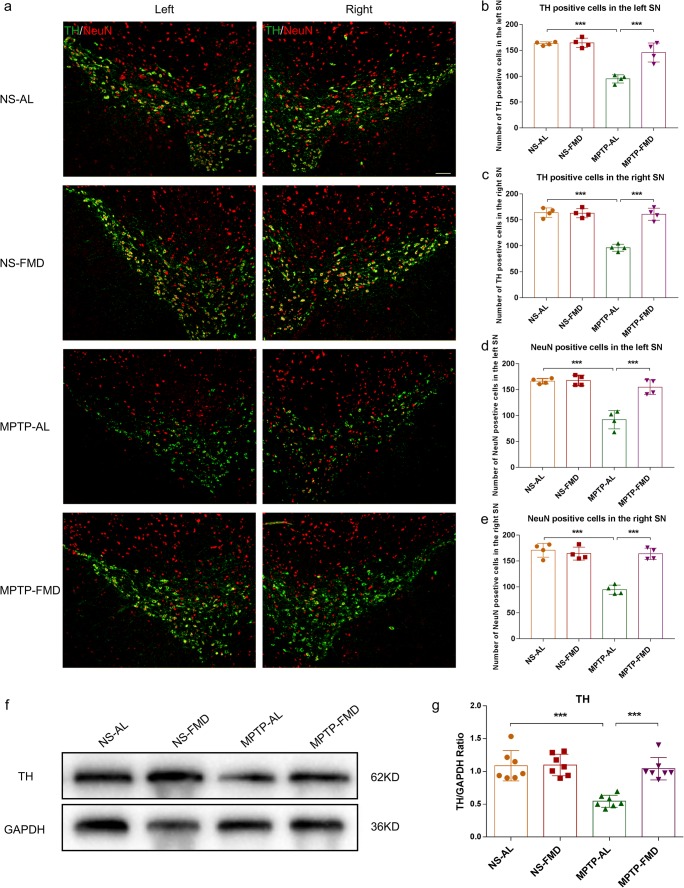
Fig. 3.
FMD treatment of PD mice prevents the MPTP-induced loss in brain dopaminergic neurons and reduction of TH expression. (a) Representative immunofluorescence staining for TH and NeuN in the right and left SN respectively. Scale bar is 100 μm. (b) Quantitative analysis of the number of TH-positive cells in the left SN, F3,12 = 34.100, p < 0.001, n = 4 mice per group. (c) Quantitative analysis of the number of TH-positive cells in the right SN, F3,12 = 51.657, p < 0.001, n = 4 mice per group. (d) Quantitative analysis of the number of NeuN-positive cells in the left SN, F3,12 = 32.374, p < 0.001, n = 4 mice per group. (e) Quantitative analysis of the number of NeuN-positive cells in the right SN, F3,12 = 38.919, p < 0.001, n = 4 mice per group. (f) Representative western blot of striatal TH expression. (g) Band intensity was quantified with the ImageJ software and quantitative data for TH following normalization to GAPDH, F3,24 = 16.732, p < 0.001, n = 7 mice per group. Statistical comparison by one-way ANOVA with post hoc comparisons of LSD; data represent the means ± SEM; **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001