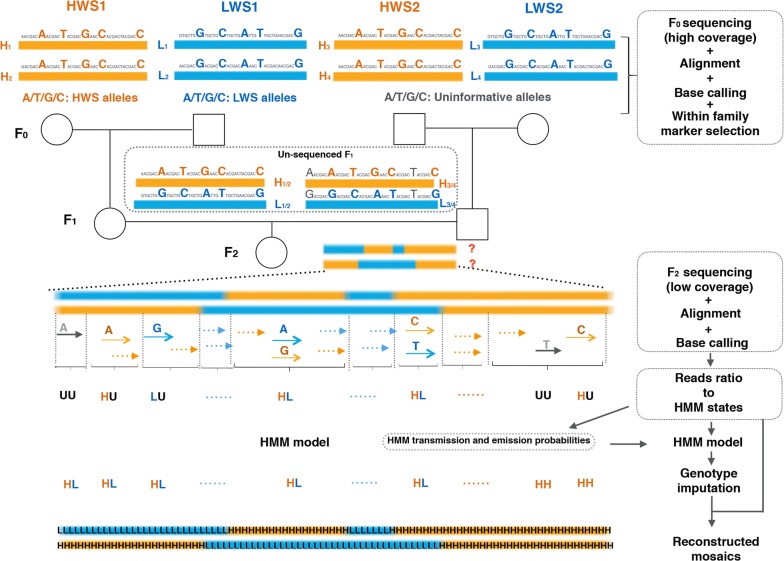
Fig. 1.
Reconstruction of the founder mosaic genotypes in an F2 individual from a multi-parent F0–F2 family with outbred (heterozygous) founders, using low-coverage sequence data. Informative markers (blue/yellow large font) are identified based on their fixation for alternative alleles in the pairs of deep-coverage sequenced F0 founders from the divergent lines (HWS1 and HWS2 vs. LWS1 and LWS2) in the family. Blue and yellow bars represent chromosomes that originate from the high (yellow) and low (blue) founder lines, respectively. Uninformative markers that segregate in at least one founder (black small font) are discarded from further analyses. The F1 individuals used as parents for the intercross (F2) offspring do not need to be sequenced, as they are heterozygous for all selected informative markers. The F2 individuals are sequenced to low-coverage and the reads are mapped to the selected informative markers. Then the founder mosaic genotypes (illustrated for one autosome by the blue and yellow bars) are inferred across the genome using the read mappings to the within-family informative markers using a Hidden Markov Model (HMM) developed for this task for inbred line crosses [7]