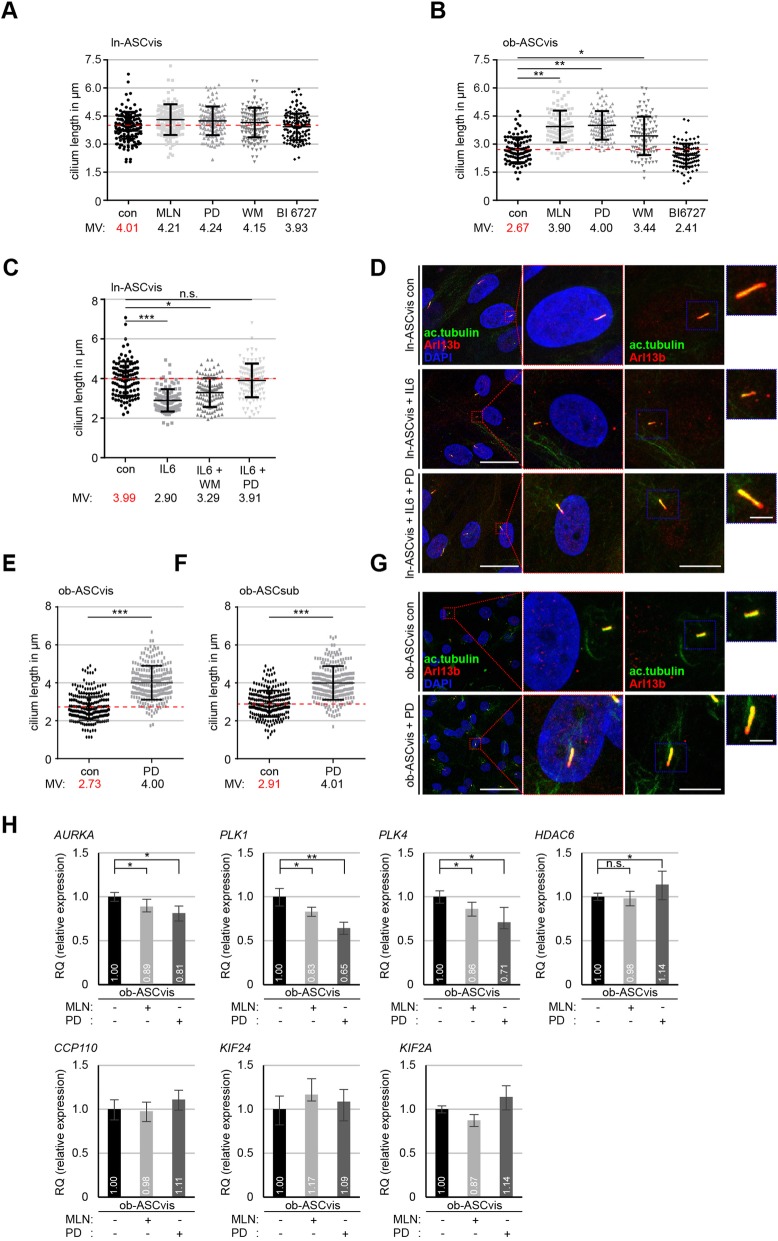
Fig. 1.
Treatment with MLN8054 or PD98059 rescues cilium length and reduces the expression level of deciliation genes like Aurora A, PLK1, and PLK4 in obese ASCs. a, b The cilium length was measured in visceral ln-ASCs and ob-ASCs treated with MLN8054 (MLN, 15 nM), PD98059 (PD, 25 nM), Wortmannin (WM, 15 nM), and BI 6727 (15 nM). The results are based on three experiments using ASCs from three obese and three lean donors (n = 100 cilia for each group) and presented as scatter plots. Red dashed line indicates the cilium mean length of control cells. c Evaluation of the cilium length in visceral ln-ASCs treated with IL6 or IL6 in combination with WM or PD. The results are based on three experiments using ASCs from three lean donors (n = 100 cilia for each group). d, g Lean (D) or obese (G) visceral ASCs were stained as indicated. Representatives are shown. Scale bar, 30 μm. Magnified representatives scale bar, 4 μm. Inset scale bar, 3 μm. e, f Quantification of visceral and subcutaneous obese ASCs treated with PD inhibitor. The results are based on six experiments using ASCs from six obese donors (n = 230 cilia for each group). h The gene levels of deciliation molecules (AURKA, PLK1, PLK4, HDAC6, CCP110, KIF24, and KIF2A). The data are based on three experiments and presented as mean ± SEM. RQ, relative quantification of gene expression. Scatter plots were used to show the mean and the minimal to maximal range of the values in a–f. Unpaired Mann-Whitney U test for a, b, c, e, and f. Student’s t test for h. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001