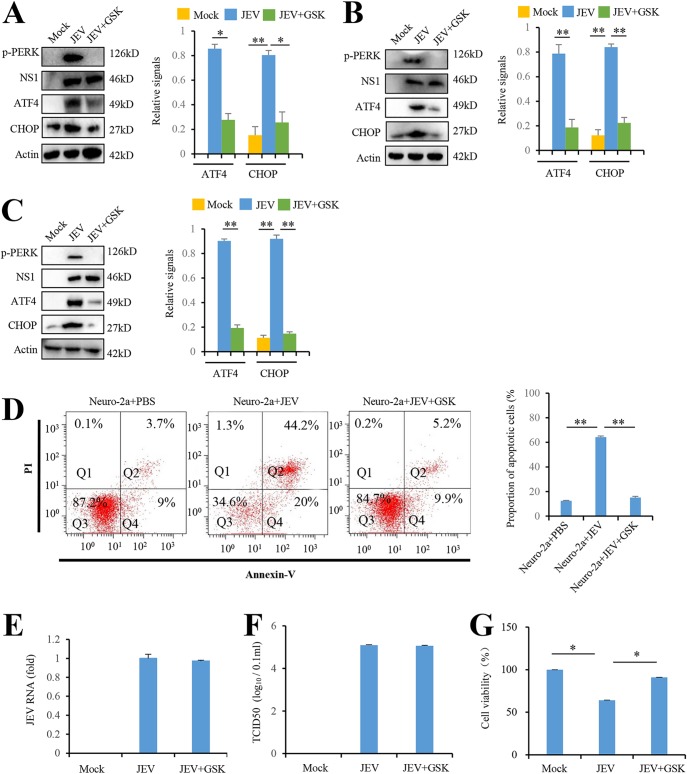
FIG 2.
JEV infection induces apoptosis by activating the PERK-ATF4-CHOP pathway. (A and B) JEV infection activates the PERK-ATF4-CHOP pathway in Neuro-2a cells (A) and BHK-21cells (B). Cells were infected with P3 strain at an MOI of 5 and treated with GSK2606414 (0.8 nM) as indicated. Mock-infected cells were used as controls. After 3 days, the cells were subjected to immunoblot analysis using JEV NS1, phospho-PERK, CHOP, ATF4, or actin antibodies. Mock-infected cells were used as controls. (C) JEV infection activates the PERK-ATF4-CHOP apoptosis pathway in mice brains. The tissues from JEV-infected and mock-infected mice brains at 3 days postinfection were collected and analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies against JEV NS1, phospho-PERK, CHOP, ATF4, or actin. (D to G) JEV infection in Neuro-2a cells induces apoptosis via PERK. Neuro-2a cells were infected with P3 strain at an MOI of 5 and treated with GSK2606414 (0.8 nM) as indicated. Mock-infected Neuro-2a cells were used as controls. After 3 days, the cells were subjected to apoptosis analysis (D), virus replication analysis (E and F), and cell viability analysis (G). Apoptosis analysis was performed with an annexin V-EGFP/PI apoptosis detection kit and analyzed by flow cytometry. Q1, Q2, Q3, and Q4 represent PI-positive, annexin V-/PI-positive, annexin V/PI-negative, and annexin V-positive cells, respectively. Virus replication was analyzed by real-time RT-PCR using JEV-specific primers and a TCID50 assay. Cell viability was analyzed by an MTT assay. Left panels (A to D) show representative images; right panels (A to D) show quantitation data. Error bars indicate the SD of the mean (n = 3). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01.