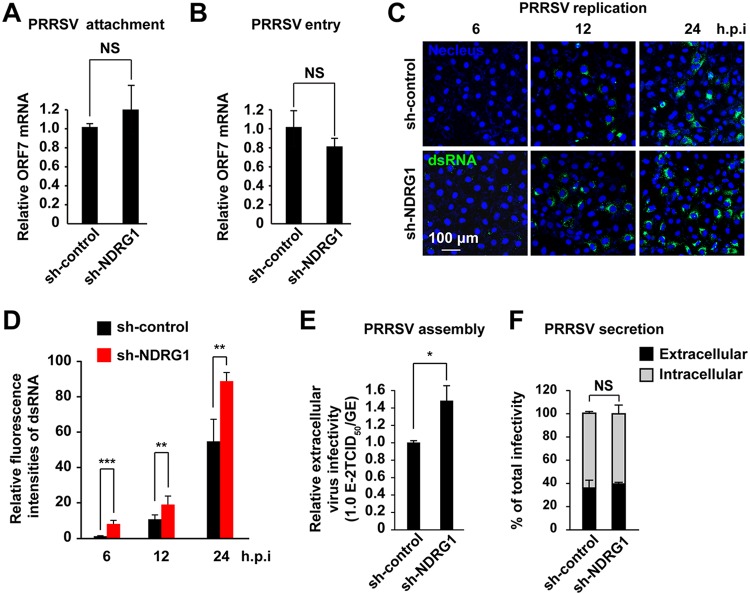
FIG 5.
NDRG1 knockdown increases PRRSV replication and assembly. (A) PRRSV BJ-4 (MOI = 10) was allowed to bind to the surfaces of sh-control and sh-NDRG1 cells on ice for 1 h. After the cells were washed with PBS, the viral RNA was isolated and quantified by RT-qPCR with ORF7-specific primers. NS, not significant (by an unpaired two-tailed t test). (B) PRRSV BJ-4 (MOI = 10) was allowed to bind to the surfaces of sh-control and sh-NDRG1 cells on ice for 1 h (binding), and cells were then shifted to 37°C for 2 h (internalization). Intracellular viral RNA was isolated and quantified by RT-qPCR using ORF7-specific primers. NS, not significant (by an unpaired two-tailed t test). (C) Cells were infected with PRRSV BJ-4 at an MOI of 10 for the indicated times, before the cells were fixed and stained for double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) and with DAPI. Random fields of view were recorded with a confocal microscope. (D) Fluorescence intensities of dsRNA in panel C were quantified in cells containing PRRSV dsRNA. (E) Cells were infected with PRRSV BJ-4 at an MOI of 10 for 24 h. The efficiency of viral assembly in the supernatants was determined by comparing the infectious titers (TCID50 per milliliter) with the total PRRSV genome equivalents (GE). *, P < 0.05 (by an unpaired two-tailed t test). (F) Cells were infected with PRRSV BJ-4 at an MOI of 10 for 24 h. The efficiency of virus secretion was determined as the ratio of intra- and extracellular infectivity relative to the total infectivity. NS, not significant (by an unpaired two-tailed t test).