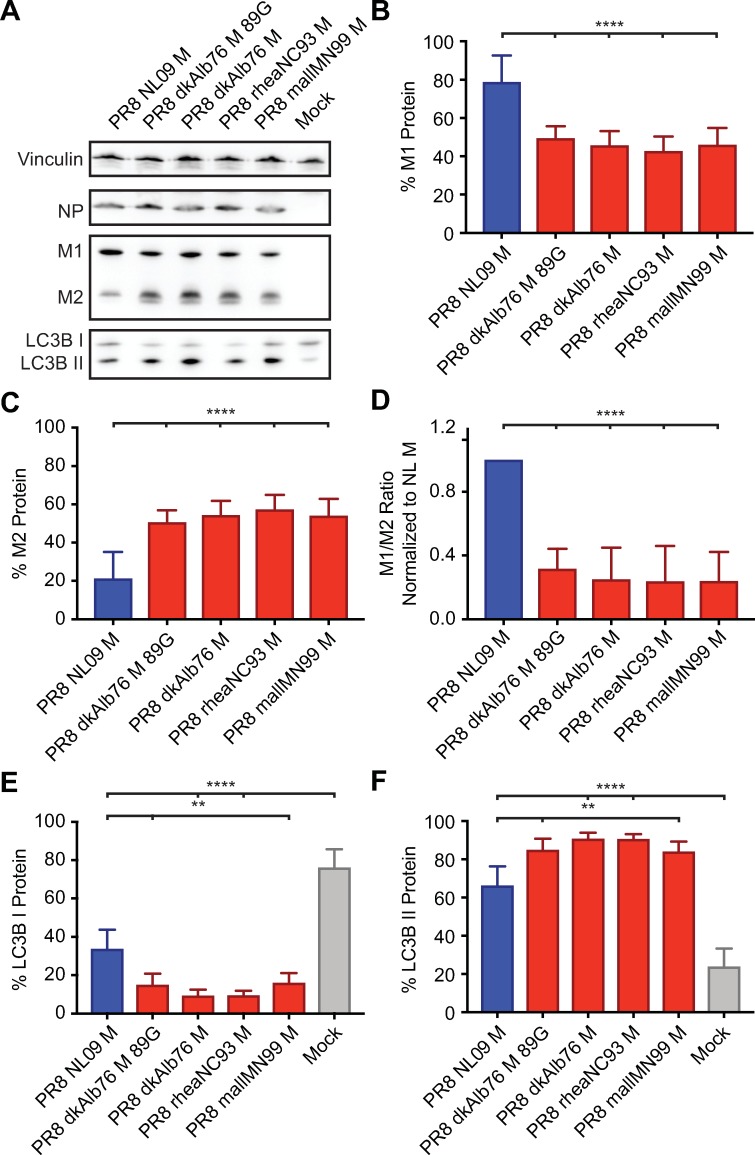
Fig 5. High expression ratio of M1 to M2 protein in A549 cells is dependent upon viral M segment host origin.
A549 cells were inoculated at a MOI of 5 PFU/cell with PR8 viruses encoding avian or human-derived M segments and incubated at 37°C for 8 h, then lysed. Western immunoblot analysis of virus-infected A549 cells: (A) Vinculin expression was measured to allow normalization of viral protein levels. NP expression was measured to assess viral replication. Levels of M1 and M2 protein expression were assessed using an antibody (Mab E10) to a common epitope at the amino terminus of M1 and M2 proteins, allowing relative expression to be assessed. Levels of LC3B I and II were assessed using an antibody that detects both the precursor and activated forms of LC3B protein. (B) M1 protein and (C) M2 protein were normalized to vinculin, quantitated and displayed as a percentage of total protein expressed from the M gene. (D) The ratio of M1:M2 protein expression. (E) LC3B I protein and (F) LC3B II protein were normalized, quantitated and displayed as a percentage of total LC3B protein. Graphs in B-F show the means with SD from three independent experiments. For each experiment, two replicate Western immunoblots were performed and quantitated. Statistical significance was assessed using ordinary one-way ANOVA.