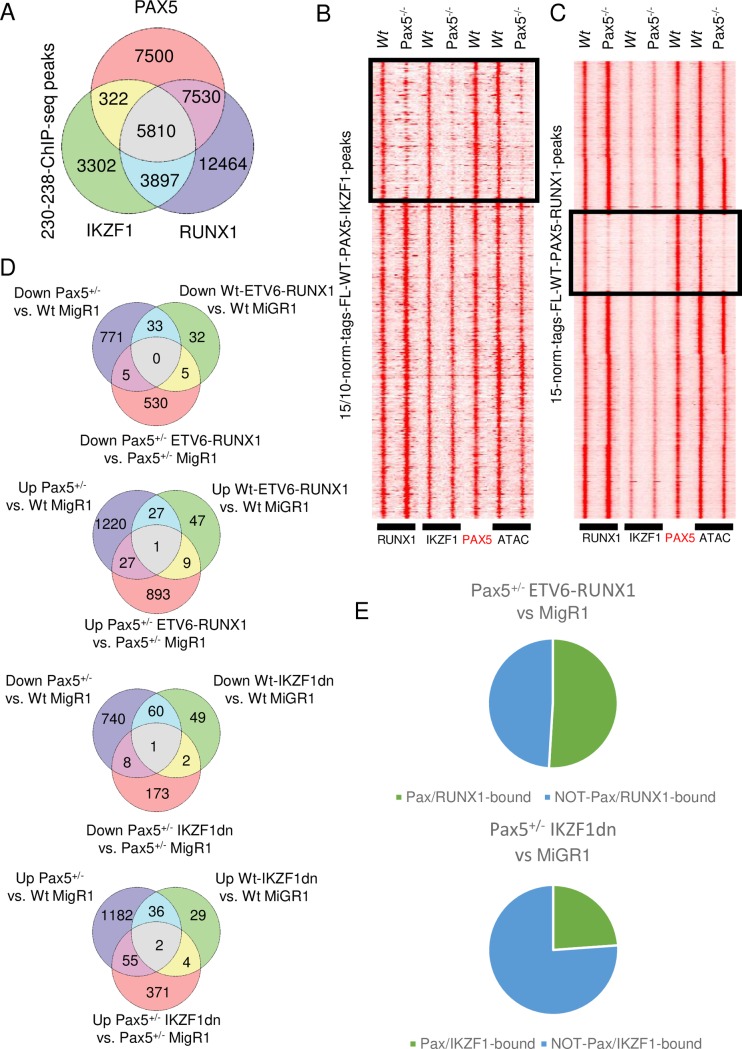
Fig 3. PAX5 is a coordinator of a transcription factor network in pro-B cells.
Panel (A) display a Venn-diagram of ChIP-seq peaks based on PAX5, IKZF1 and RUNX1 ChIP seq analysis using the 230–238 Pre-B cell line. Peaks were called using the HOMER platform (findPeaks -style factor) and resulting files were filtered for peaks ≥15 normalized tags. Overlapping peaks were identified using the mergePeaks command in HOMER. (B-C) Heat maps displaying overlapping PAX5 and IKZF1 or RUNX1 binding sites as defined by ChIP-seq analysis of in vitro expanded Wt Pro-B cells. Peaks were identified using HOMER (findPeaks -style factor) and filtered for ≥15 (PAX5, RUNX1) or ≥10 (IKZF1) normalized tags. Overlapping peaks were identified using the mergePeaks command in HOMER. ChIP-seq and ATAC-seq (GSE92434) (43) signals were visualized in heatmaps with data obtained from primary in vitro expanded Wt or Pax5-/- mouse Pre-B cells as indicated. Heatmaps were clustered in Cluster3 using average linkage uncentered correlation. (D) Venn diagrams displaying results from RNA-seq experiments from primary in vitro expanded FL-Wt and Pax5+/- Pre-B cells transduced with retroviruses encoding either a dominant negative form of IKZF1 (IKZF1-dn), an ETV6-RUNX1 or a control vector (pMIG). Differentially expressed genes (FDR ≤ 0.05, foldchange ≥ 2) were identified using HOMER as described in materials and methods. (E) Pie-charts displaying the fraction on genes differentially expressed in ETV6-RUNX1 or IKZF1dn as compared to MIGR1 transduced Pax+/- cells that can be defined as direct target genes for the transcription factors. Definition of target genes were based on proximity annotation of IKZF1 and RUNX1 peak files merged with PAX5 peaks from 230–238 Pre-B cells to identify IKZF1 and PAX5 or RUNX1 and PAX5 co-bound genes.