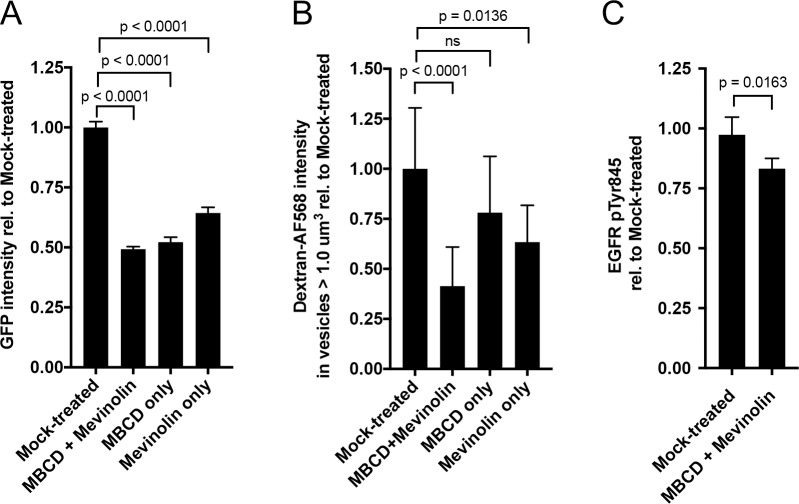
Fig 10. Effect of cholesterol depletion on RSV infection.
A549 cells were cholesterol-depleted by treatment with methyl-beta-cyclodextrin (MBCD) and Mevinolin or each chemical separately. (A) RSV infection of cholesterol-depleted A549 cells. A549 cells were pre-treated for 5 h with the indicated cholesterol-depleting compounds and infected with RSV-GFP (MOI = 1 PFU/cell) with presence of the cholesterol-depleting compounds maintained. Viral GFP expression was quantified 17 h p.i. and reported relative to mock-treated infected cells. (B) Quantification of macropinocytosis in cholesterol-depleted RSV-infected A549 cells. A549 cells were pre-treated for 16 h with the indicated cholesterol-depleting compounds in the absence of serum and infected with RSV (MOI = 5 PFU/cell) in the presence of dextran-AF568. At 5 h p.i the cells were fixed with 5% PFA and nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. The total intensity of dextran-AF568 in vesicles larger than 1.0 μm3 was quantified (Materials and Methods) and reported relative to mock-treated infected cells. The statistical significance of the differences was determined by one-way analysis of variance with Tukey’s multiple-comparison post-test and p-values are indicated (ns, not significant). (C) EGFR Tyr845 phosphorylation in cholesterol-depleted cells. A549 cells were treated with MBCD and Mevinolin for 16 h to deplete cholesterol from the plasma membrane. Cells were infected with wt RSV (MOI = 5 PFU/cell) and the phosphorylation of EGFR Tyr845 was quantified by an EGFR phosphorylation antibody array, as described in Fig 8. The level of pTyr845 was reported relative to mock-treated infected cells. The statistical significance of difference was determined by a two-tailed unpaired t-test.