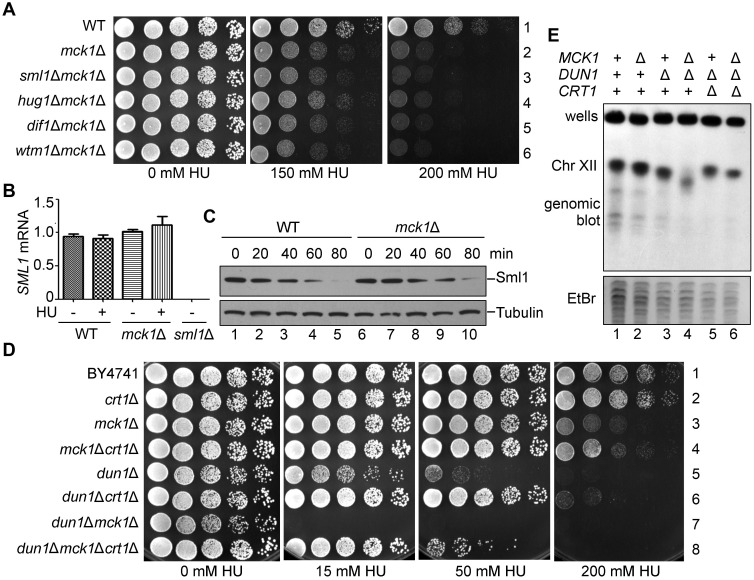
Fig 2. crt1Δ, but not sml1Δ, suppresses the checkpoint deficiency of mck1Δ.
(A) Deletion of SML1, DIF1 or WTM1 has no apparent suppression of the HU sensitivity of mck1Δ. WT, mck1Δ, mck1Δsml1Δ, mck1Δdif1Δ, mck1Δwtm1Δ (S1 Table) were tested for the growth in the presence of the indicated concentrations of HU by serial dilution analysis as described in Fig 1A. (B) Measurement of the SML1 mRNA levels in mck1Δ by qPCR. Cells were grown in rich media with or without 200 mM HU for 3 h. The total mRNA was prepared as described in Methods and Materials. The relative levels of SML1 to ACT1 mRNAs were determined by qPCR analyses. Error bars represent standard deviations from at least three biological repeats. No significance was found by the student t-test. (C) Mck1 is not involved in Sml1 degradation. The Sml1 protein levels in mck1Δ were examined after 200 mM HU treatment for the indicated times. YFP-Sml1 and Tubulin were detected by immunoblots. (D) CRT1 deletion partially suppresses the HU sensitivity of mck1Δ and mck1Δdun1Δ. WT, crt1Δ, mck1Δ, mck1Δcrt1Δ, dun1Δ, dun1Δcrt1Δ, dun1Δmck1Δ, dun1Δmck1Δcrt1Δ (S1 Table) were tested for the HU sensitivity by serial dilution analysis as described in (A). (E) Mck1 and Dun1 play non-redundant roles in the rDNA copy number maintenance. Genomic DNA was prepared in an agar plug and separated on a 1% agarose pulsed-field gel. Ethidium bromide staining of yeast chromosomes is shown in the lower panel. Upper panel shows chromosome XII by hybridization with a probe against 18S rDNA.