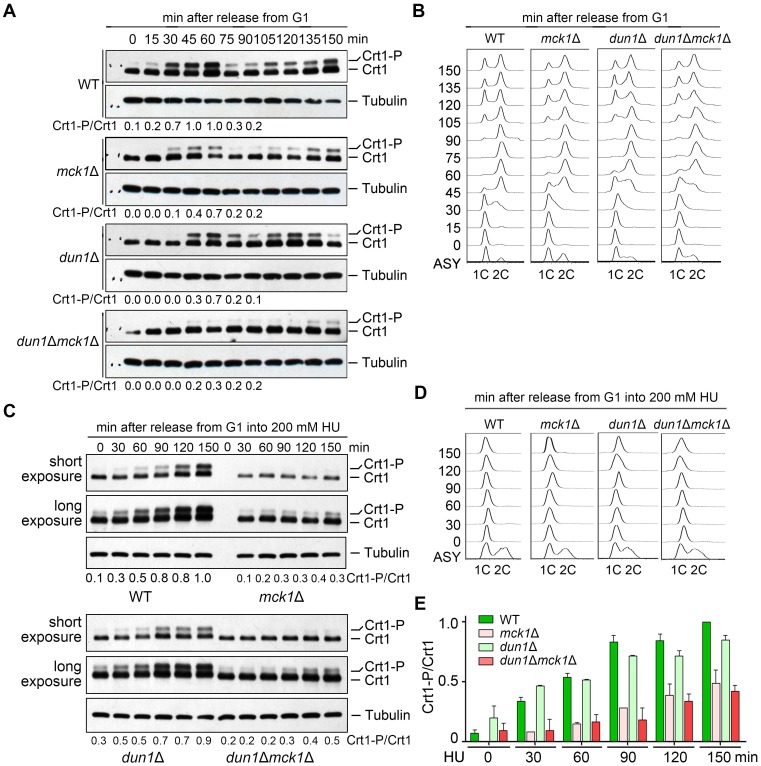
Fig 3. Mck1 is responsible for both cell-cycle-dependent and HU-induced Crt1 phosphorylation.
(A) Phosphorylation of Crt1 in normal S phase. Cells were synchronized in G1 by α-factor before releasing into fresh media for the indicated times. The cell cycle progression was analyzed by FACS. Lysates were prepared from WT and mck1Δ cells. The protein levels of Crt1-13Myc were detected by immunoblots using an anti-Myc antibody as described as in Fig 2D. The Crt1-P/Crt1 ratio was indicated below each lane for the first cell cycle. (B) A representative cell cycle profile of the samples used for time-course analysis of Crt1 phosphorylation in (A). (C) HU-induced Crt1 phosphorylation. Cells were synchronized in G1 by α-factor before release into fresh media containing 200 mM HU for the indicated times. The cell cycle progression was analyzed by FACS. Lysates were prepared from WT and mck1Δ cells. The protein levels of Crt1-13Myc were detected by immunoblots using an anti-Myc antibody as described as in Fig 2D. See S3C Fig for the results of biological repeats. (D) A representative cell cycle profile of the sampled used in (C). (E) Quantitation of the relative levels of Crt1 phosphorylation from biological repeats.