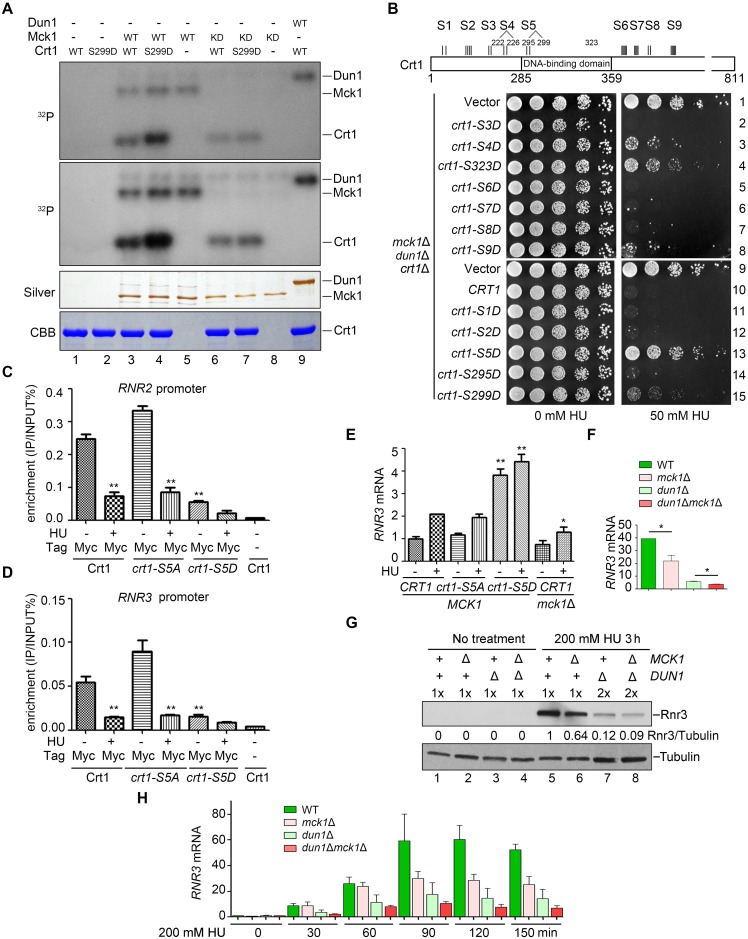
Fig 4. Crt1 phosphorylation affects its binding to the promoters of RNR genes and thereby reduces RNR induction.
(A) Crt1 serves as a substrate of Mck1. In vitro kinase assays were performed using Mck1-5FLAG, Mck1-KD (D164A), or Dun1 and substrate His6-Crt1-(201–453) or His6-Crt1-(201–453)-S299D in the presence of ɣ-32P-ATP. After resolved in an 8% polyacrylamide gel with SDS, the samples were subjected to autoradiography. Then, the gel was stained by Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB) to show the amount of the loaded protein in each reaction. Note that WT Mck1 and Dun1 show auto-phosphorylation activities. (B) A schematic diagram of the consensus Mck1 kinase recognition motifs in Crt1. Crt1 bears eight clusters of (S/T)-X-X-X-(pS/T)*, where * stands for the priming phosphorylated residue and X for any amino acid. S1 (S58, S62); S2 (S167, S171, S173, S174); S4 (S222, T226); S5 (S295, S299); S6 (S388, S389, S391, S393, S394); S7 (S412, S414, T416, S418); S8 (T488, S492); S9 (S556, S558, S560, S562). S3 (T197, T199) phosphorylation is detected by MS, whereas S323 represents the putative Mec1 site. Phospho-mimic mutations of several putative Mck1 sites in Crt1 rescue the HU sensitivity of mck1Δdun1Δ to a similar extent as crt1Δ. The dun1Δmck1Δcrt1Δ triple mutant was transformed with pRS313 vector, WT CRT1 or the indicated mutants. Five-fold dilution of the cells was grown at 30°C for 48 h. (C) ChIP-qPCR assays of Crt1 localization at the RNR2 promoter in various alleles in the presence or absence of 200 mM HU. (D) ChIP-qPCR assays of Crt1 localization at the RNR3 promoter in various alleles in the presence or absence of 200 mM HU. (E, F) Measurement of the RNR3 mRNA levels in various mutants by qPCR. Cells were grown in rich media with or without 200 mM HU for 3 h. The total mRNA was prepared as Methods and Materials. The relative levels of RNR3 to ACT1 mRNAs were determined by qPCR analyses. The value of untreated WT was set to 1.0. Error bars represent standard deviations from at least three biological repeats. P-value <0.01 and 0.05 are donated as “**” and “*”, respectively. (G) Western blotting of the Rnr3 protein levels in various mutants with or without 200 mM HU treatment for 3 h. Mck1 is necessary for efficient Rnr3 induction. Cells were grown and treated as above. Rnr3-13Myc and Tubulin were detected by immunoblots. (H) Time course measurement of the RNR3 mRNA levels by RT-PCR after HU treatment for the indicated time. Three biologically repeated experiments were basically performed as described in (E).