Fig. 1.
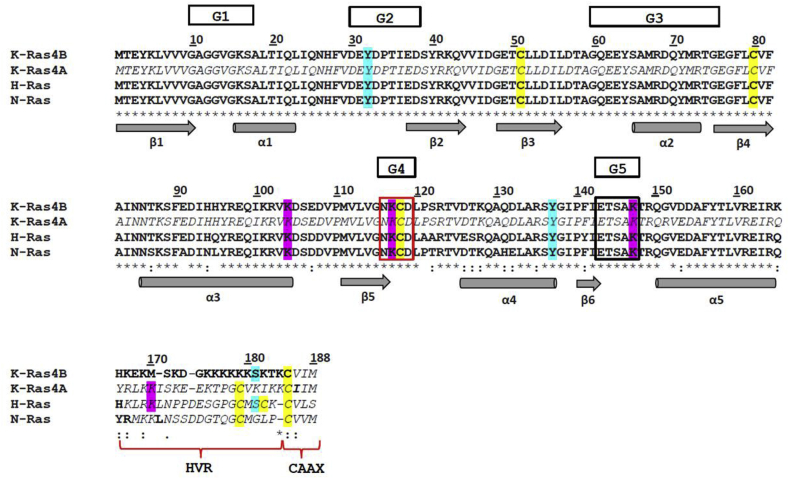
Multiple amino acid sequence alignment of K-Ras4B (PDB ID code: 5TAR, chain A) [30], K-Ras4A (UniProtKB entry: P01116-1) [32], H-Ras (PDB ID code: 5 X 9S) [33], and N-Ras (PDB ID code: 3CON) (Reid et al., 2017). The amino-acid sequences have been aligned with CLUSTAL omega [107] using the BLOSUM62 substitution matrix [108] to score both pairwise and multiple alignment. In bold are reported the amino acid residues building up the three-dimensional structures of K-Ras4B, H-Ras, and N-Ras respectively. The three-dimensional structure of K-Ras4A is not available. In italic are highlighted the amino acid residues of K-Ras4A and those of K-Ras4B, H-Ras, and N-Ras that are not solved in the three-dimensional structures. The amino acid residues that undergo post-translational modifications are indicated with different colors: Cys residues are in yellow, phosphorylated Tyr are in light blue, and ubiquitylated Lys are in pink. The NKCD (i.e., G4) and the ETSAK (i.e., G5) motifs have been boxed in red and black, respectively. The HVR domain and the CAAX motif are also shown. The G1-G5 loops that catalyze the GTP hydrolysis are evidenced. The arrows indicate the β-strands and the cylinders the α-helices. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)