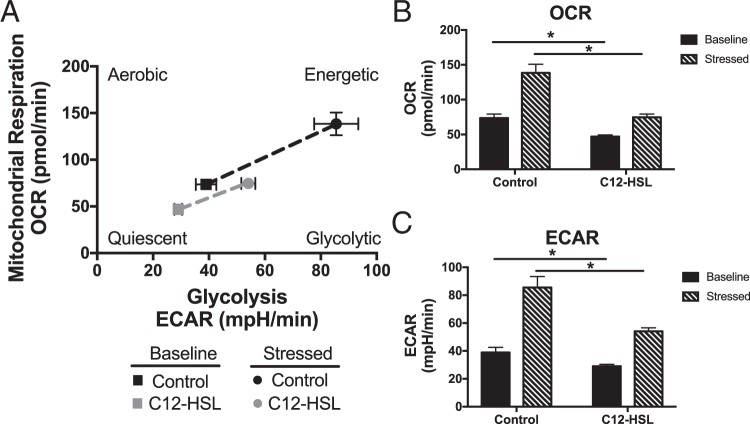
Figure 2.
P. aeruginosa QS molecules disrupt bronchial epithelial cell bioenergetics and metabolic potential. BEAS-2B cells were treated with vehicle control (DMSO) or 100 μM 3-oxo-C12-HSL for 6 hours. Cells were then analyzed using Seahorse Cell Energy Phenotype assay. This allows for the real time measurement of oxygen consumption rate (OCR) and extracellular acidification rate (ECAR), which are representative of mitochondrial respiration and glycolysis respectively, at rest and after induction of a bioenergetic stress caused by treatment with the ATP synthase inhibitor, oligomycin, and the uncoupling agent, FCCP. (A) Plot of baseline and stressed conditions in control and 3-oxo-C12-HSL-treated cells. 3-oxo-C12-HSL-treated cells are more quiescent at baseline and have less metabolic potential under stressed conditions. (B) OCR measurements at baseline and stressed conditions. 3-oxo-C12-HSL decreases basal and stressed OCR as compared to control. (C) ECAR measurements at baseline and stressed conditions. 3-oxo-C12-HSL decreases basal and stressed ECAR as compared to control. Results are mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, n = 3 independent experiments. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test used for statistical analysis.