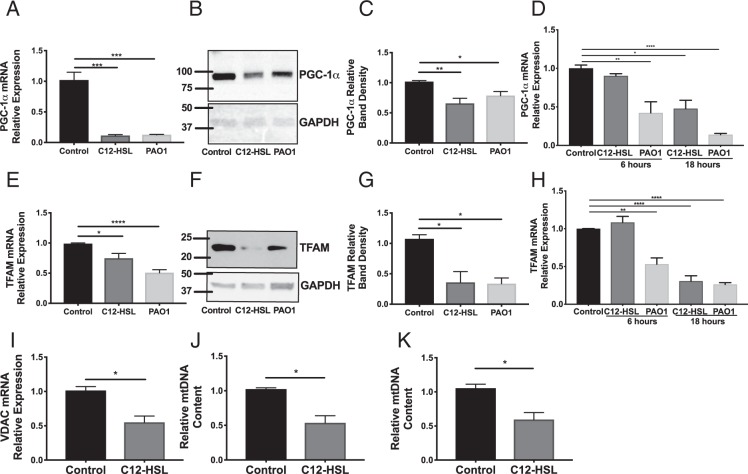
Figure 4.
P. aeruginosa infection and the bacterial QS molecule attenuates expression of PGC-1α and TFAM and reduces mitochondrial biogenesis in bronchial epithelial cells. (A–C,E–G,I–J) BEAS-2B cells were treated with 100 μM 3-oxo-C12-HSL or infected with PAO1 (MOI 1) for 16 hours. Relative mRNA (A,E,I) and protein expression (B,F for representative western blots, (C,G for normalized densitometry) of PGC-1α (B,C) and TFAM (F,G) were measured. The full-length blots are presented in Supplementary Figs 1 and 2. Both PAO1 and 3-oxo-C12-HSL significantly attenuated expression of PGC-1α and TFAM in BEAS-2B cells. (D,H,K) Human primary bronchial epithelial cells (NhBEs) grown at an air-liquid interface were also treated with 100 μM 3-oxo-C12-HSL or infected with PAO1 (MOI 1) for 6 and 18 hours and relative mRNA expression for PGC-1α (D) and TFAM (H) were measured. PAO1 attenuated expression of PGC-1α and TFAM at both 6 and 18 hours. 3-oxo-C12-HSL attenuated expression of PGC-1α and TFAM at 18 hours. (I) In BEAS-2B cells, 3-oxo-C12-HSL reduced relative mRNA expression of the mitochondrial marker VDAC1. In BEAS-2B cells (J) and NhBEs (K) 3-oxo-C12-HSL reduced relative mtDNA content normalized to nuclear DNA. Results are mean ± SEM. * p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001 by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test, n = 6–8 independent experiments (A,C,E,G,I) n = 3 independent experiments (D,H). For (I,J,K) results are mean ± SEM.*p < 0.05 by unpaired t test, n = 3 independent experiments.