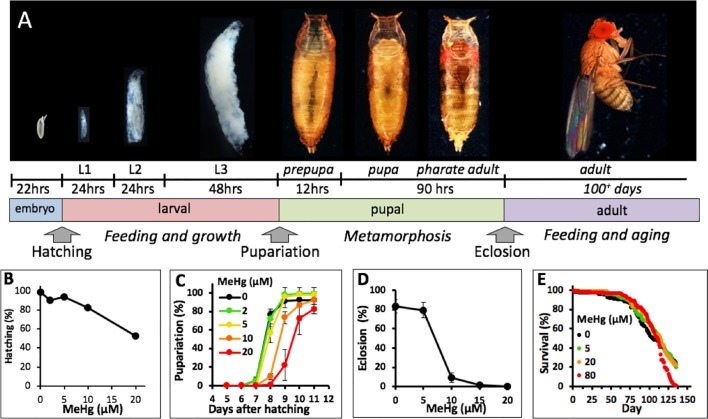
Figure 1.
Drosophila life cycle and toxicity endpoints of MeHg. (A) Drosophila development from embryo to adult is holometabolous and progresses through intermediate larval and pupal stages. Approximate development times for each stage at 25°C and transitional events that can be scored (e.g., hatching, pupariation and eclosion) are indicated. (B–D) Various endpoint assays for the effects of developmental MeHg exposure. Canton S flies were used in all assays. (B) Larval hatching rate of embryos collected from a mating population of flies fed on the indicated concentration of MeHg food (Reproduced from Rand et al., 2008). (C) Rate of pupariation of larvae reared from the L1 stage on the indicated concentration of MeHg food. (D) Rate of eclosion of pupae reared on MeHg food at the indicated concentration throughout the larval stages. (E) Survival rate of adult flies reared on MeHg-free food from the larval stage and transferred to food with indicated MeHg concentration after 2–3 days after eclosion.