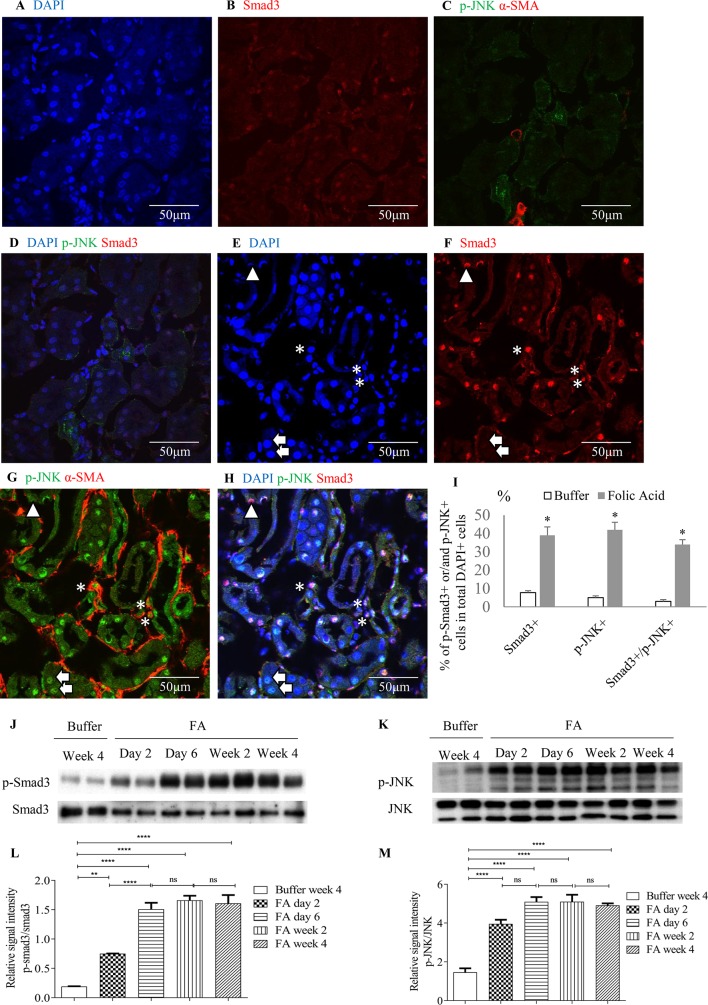
Figure 2.
Smad3 and JNK signaling activation after folic acid (FA)–induced acute kidney injury. Confocal microscopy demonstrated same fields in buffer-treated kidney (A–D) or kidney 6 days after folic acid treatment (E–H). (A) DAPI, blue. (B) Nuclear staining of Smad3, red. (C) p-JNK, green and α-SMA, red. (D) Merged with DAPI (blue), nuclear staining of Smad3 (red) and p-JNK (green). (E) DAPI, blue. (F) Nuclear staining of Smad3, red. (G) p-c-Jun N-terminal kinases (JNK), green and α-SMA, red. (H) Merged with DAPI (blue), nuclear staining of Smad3 (red) and p-JNK (green). Arrows indicate nuclear Smad3(−)/p-JNK(+) cells; arrow head shows a nuclear Smad3(+)/p-JNK(−) cell; asterisks show interstitial α-SMA(+)/nuclear Smad3(+)/p-JNK(+) cells. (I) Quantification of nuclear staining of nuclear Smad3(+), p-JNK(+), and nuclear Smad3(+)/p-JNK(+) cells. *P < 0.05 vs. buffer-treated kidney. Western blotting shows p-Smad3 (J) and p-JNK (K) in kidneys 2 days, 6 days, 2 weeks, and 4 weeks after folic acid or buffer injection. Quantification of relative signal intensities of p-Smad3/Smad3 (L) and p-JNK/JNK (M) in kidneys after folic acid or buffer injection. Original magnification (×600). Data are mean ± SD (n = 6/group). **P < 0.01; ****P < 0.0001; ns, not significant.