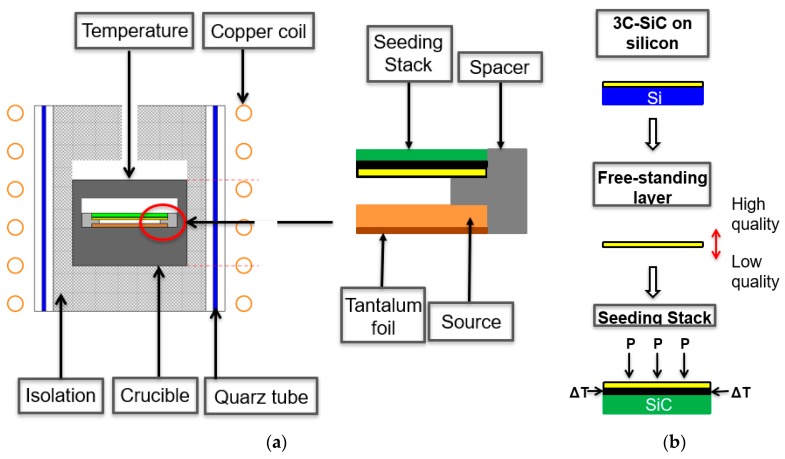
Figure 1.
(a) Schematic of the used vertical physical vapor transport (PVT) reactor on the left and the hot zone on the right. Starting from the bottom of the hot zone, a tantalum foil is introduced as a carbon getter. On top, a polycrystalline SiC source is placed. The spacer limits the source-to-substrate distance. The final part is the self-manufactured seeding stack. (b) The manufacturing process for the seeding stack is necessary for high-temperature growth. The starting material is epitaxial 3C-SiC-on-Si grown by chemical vapor deposition (CVD). The removal of the silicon substrate is performed using wet-chemical etching by HNA (HF:HNO3:H2O) resulting in a high-quality growth front and a low-quality transition side. The final merging process is performed with a carbon glue layer (black), homogeneous pressure and a specific temperature treatment.