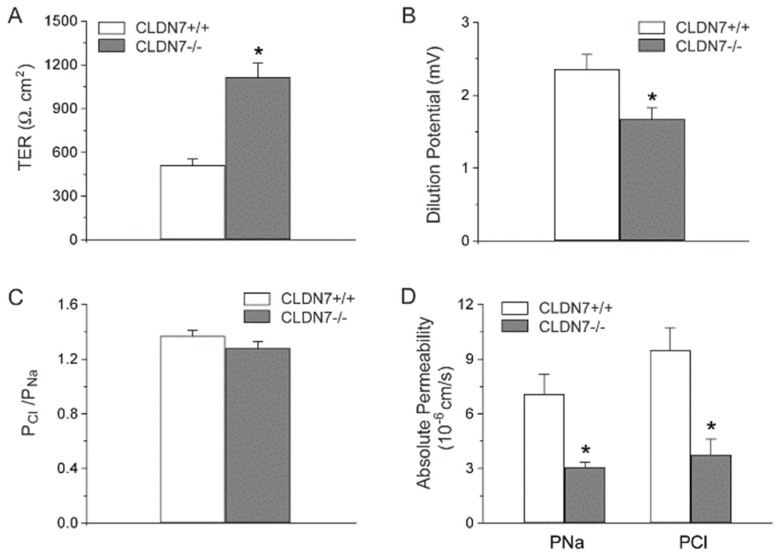
Figure 2.
Deletion of CLDN7 increased transepithelial resistance (TER) and decreased paracellular Cl− and Na+ permeability on CD cell monolayers. (A) TER was measured on monolayers cultured for 7 days. (B) CD cells were grown on collagen-coated Snapwell filters for 7 days to reach the full confluence. The filter rings containing cell monolayers were mounted into EasyMount chambers. Both apical and basal chambers were filled with buffer containing 140 mM NaCl. Subsequently, buffer in the basal chamber was replaced by 70 mM NaCl, and dilution potentials were measured. (C) The ratio of the absolute permeability of Cl- to Na+ (PCl/PNa) was calculated using the Goldman–Hodgkin–Katz equation. The ratio of PCl/PNa was >1 in CLDN7+/+, indicating that these CD cells were more permeable to Cl− than Na+. (D) The absolute permeability for PCl and PNa was calculated according to the method of simplified Kimizuka and Koketsu equations. * p < 0.05. n = 3.