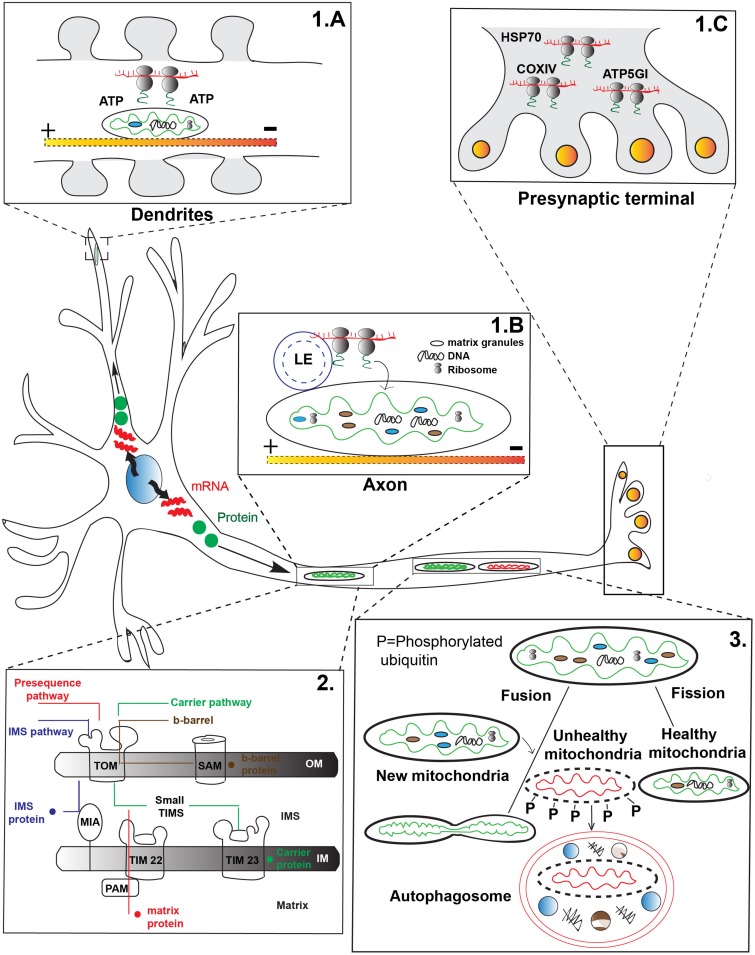
FIGURE 1.
Transport-dependent mechanisms of mitochondrial maintenance. (1) mRNAs are transported to various regions of the neuron for local translation of mitochondrial proteins. (A) mRNA transported to mitochondria can be translated for local use, such as in dendritic spines during synaptic remodeling. Mitochondria are thought to generate energy for local translation. (B) Local translation of mitochondrial proteins from mRNA transported on late endosomes (LE) that pause on a mitochondria in axons has been demonstrated. (C) Polyribosomes containing mRNAs important for mitochondrial function are found in the pre-synaptic terminal of photoreceptors, indicating active transport of the mRNAs to this site. (2) After either local protein synthesis from transported mRNAs or protein transport to mitochondria, proteins must be imported into the organelle. Four major types of mitochondrial protein import exist: Pre-sequence pathway (red) primarily for matrix proteins; Intermembrane space (IMS) protein transport pathway (blue) important for cysteine-rich IMS proteins; Carrier protein pathway (green) for transmembrane proteins in the inner membrane; and the Outer membrane (OM) β-barrel protein import pathway (brown) for transmembrane proteins destined for the OM. TOM, translocase of the outer membrane; TIM, translocase of the inner membrane; SAM, sorting and assembly machinery; PAM, pre-sequence translocase associated motor; MIA, mitochondrial intermembrane space import and assembly machinery; OM, Outer membrane; IM, Inner membrane; IMS, Inner membrane space. Yellow-red shaded line indicates microtubule in panels A,B. (3) Mitochondria undergo continuous cycles of fusion and fission to help replenish the organelle. Fusion with younger mitochondria (green) which move in the anterograde direction from the cell body is thought to replenish proteins and lipids important for mitochondrial survival. Mitochondrial fission has been postulated to remove damaged mitochondrial components for degradation (red). Mitochondria are targeted for mitophagy after fission through phosphorylation (P) dependent events.