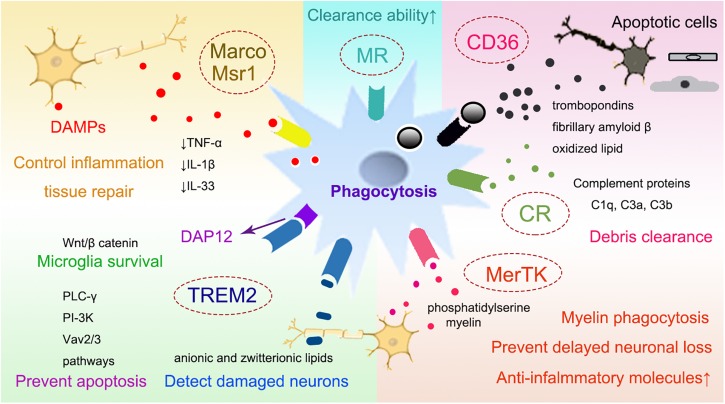
FIGURE 2.
The receptors that mediate phagocytosis of myeloid immune cells. Several receptors have been suggested to mediate the phagocytosis of myeloid cells, such as the class A scavenger receptor Marco and Msr1, the class B scavenger receptor CD36, TREM2, CRs, MRs, and MerTK. Myeloid cells can phagocytose the DAMPs released from damaged neurons with the receptors such as Msr1 and Marco, which subsequently downregulate the neurovascular inflammation and enhance brain repair. Through CD36, myeloid cells can also clear tissue debris from apoptotic cells, thrombospondins, oxidized lipid, et al. TREM2 is important for preventing microglia apoptosis, it also promotes the survival of microglia via the Wnt/β catenin pathway. Complement receptor, such as CR1 and CR3, may bind to apoptotic neuronal cells and contribute to clearing debris and limiting neuroinflammation. MerTK is associated with the myeloid phagocytosis of myelin, neurons and eryptotic erythrocytes, leading to prevent delayed neuronal loss after stroke. CD36, cluster of differentiation 36; TREM2, triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2; CRs, complement receptors; MRs, mannose receptors; MerTK, the mer receptor tyrosine kinase; DAMP, danger associated molecular pattern; Msr1, macrophage scavenger receptor 1; Marco, macrophage receptor with collagenous structure.