Fig. 1.
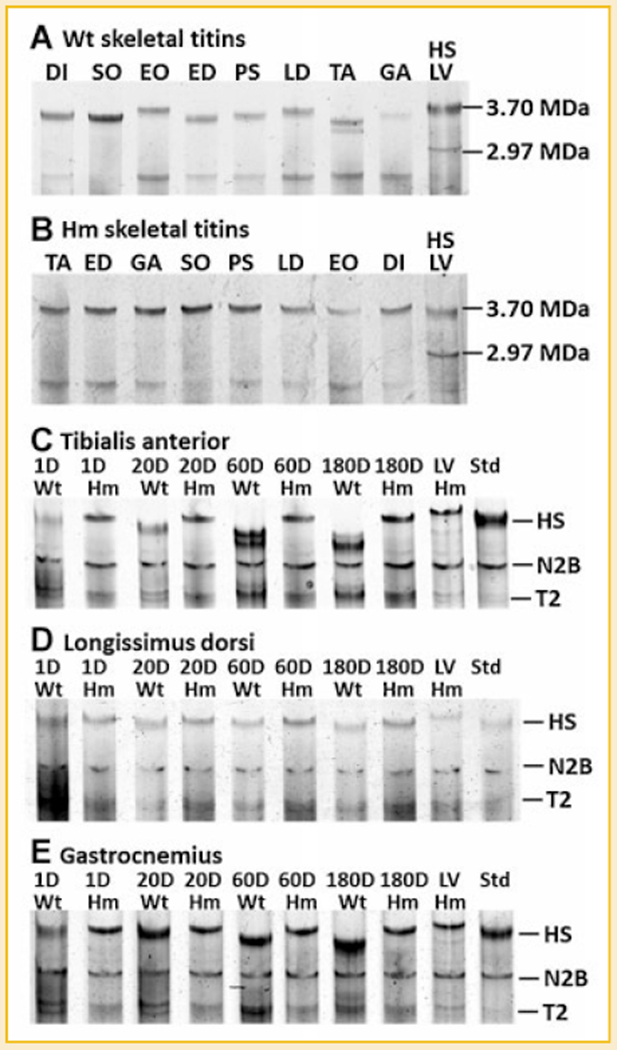
Titin isoforms in different skeletal muscles and the developmental transition of titin isoform in wild type and homozygote animals. A: The size of titin varies in different skeletal muscles of wild type rat; (B) The size of titin remains the same in all mutant skeletal muscles. A mixture of human soleus (HS, titin size of 3.7 MDa) and rat left ventricle (LV, titin size of 2.97 MDa) is included as a size ruler; (C–E) Titin isoforms in TA, LD, and GA was investigated at four time points: 1 day (D), 20, 60, and 180 days for both genotypes. Results show that titin in Wt TA and Wt GA changed dramatically from 1 to 180 days where as the Wt LD titin isoforms barely changed during this period. Titin size in mutant skeletal muscles remained constant during development. Wild type LV was mixed with each sample as a migration distance marker. HS, human Soleus; N2B, the major adult ventricle titin isoform; T2, titin proteolytic fragment.
