Fig. 3.
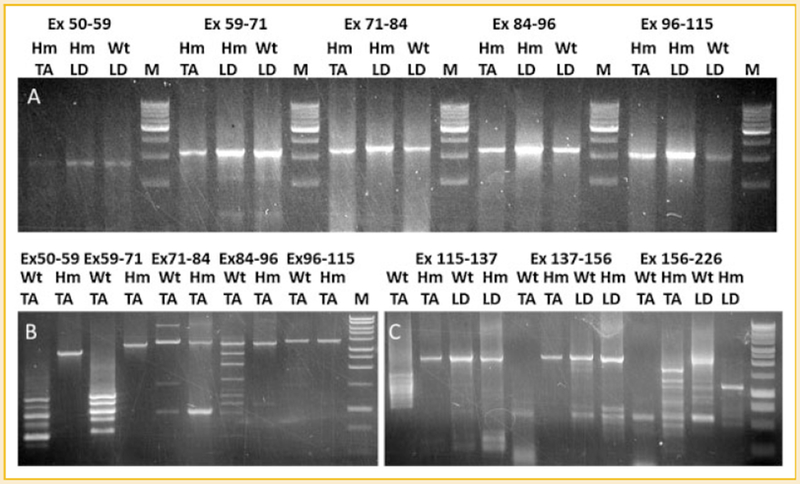
Splicing analysis of titin mRNA in wild type and mutant skeletal muscles. cDNAs from Wt TA, Hm TA, Wt LD, and Hm LD are amplified by primer sets: 50F-59R, 59F-71R, 71F-84R, 84F-96R 96F-115R, 115F-137R, 137F-156R, and 156F-226R for the corresponding exons (Ex, exon; F, forward primer; R, reverse primer). A: only constitutive splicing can be found in the middle Ig region (exon 50-115) of Hm TA, Wt LD, and Hm LD. B: alternative splicing of middle Ig region can be found in Wt TA but only constitutive splicing in Hm TA. C: Only alternative splicing can be detected in the PEVK region (exon 115-226) of Wt TA but constitutive splicing exists in wt LD, Hm LD, and Hm TA from exon 115 to 156; the region from exon 156 to 226 is alternatively spliced in all tested tissues.
