Figure 6 |. Hyperglycemia activates apoptosis signal regulated kinase 1 (ASK1)–p38 signaling in podocytes and promotes apoptosis.
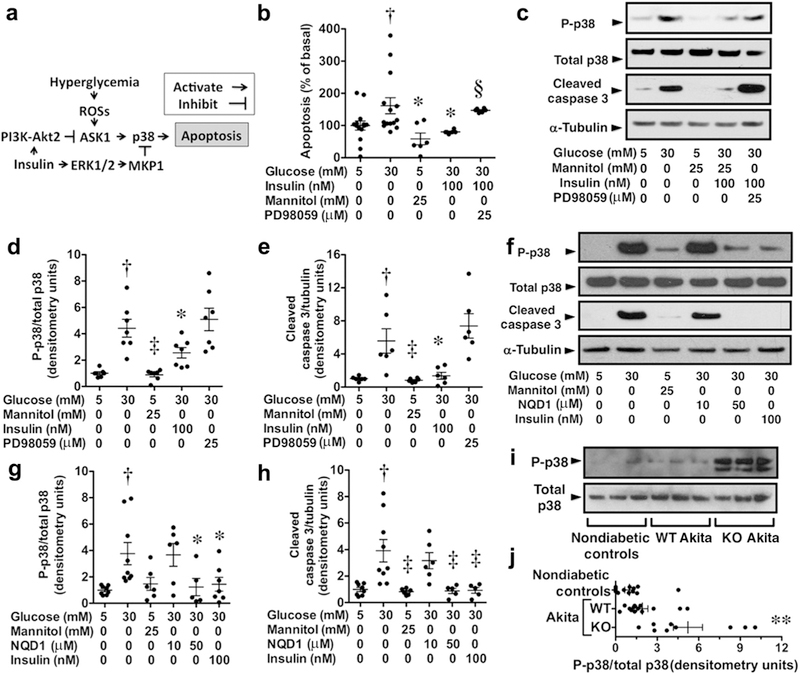
(a) ASK1 is activated by hyperglycemia-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation, which stimulates ASK1-p38 signaling and promotes cellular apoptosis.47 Insulin stimulates both phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)–Akt2 and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling, which promotes ERK-dependent inhibition of p38 signaling and PI3K-Akt2–dependent inhibition of ASK1 signaling.39,47,48,49 (b) Hyperglycemia (30 mM glucose) induced podocyte apoptosis, and this apoptotic effect was inhibited by insulin. The ERK inhibitor PD98059 blocked the antiapoptotic effect of insulin. The osmotic control (mannitol) had no significant effect on podocyte apoptosis. (c–e) Hyperglycemia (30 mM glucose) stimulated ASK1-p38 signaling (phospho-p38 or P-p38) in cultured podocytes and enhanced expression of the apoptosis marker cleaved caspase 3. Both p38 signaling and podocyte apoptosis were inhibited by insulin, and the antiapoptotic effect of insulin was inhibited by ERK inhibition with PD98059. (f–h) Hyperglycemia stimulated ASK1-p38 signaling in cultured podocytes and enhanced expression of the apoptosis marker cleaved caspase 3. Both p38 signaling and podocyte apoptosis were inhibited by insulin and the ASK1 inhibitor NQD1 (50 μM). (i,j) ASK1-p38 signaling was enhanced in knockout (KO) Akita mice compared with either nondiabetic controls or wild-type (WT) Akita mice. MKP1, mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase 1. †P < 0.05 versus 5 mM glucose, *P < 0.05 or ‡P < 0.01 versus 30 mM glucose, §P < 0.05 versus 30 mM glucose and insulin, **P < 0.05 versus either nondiabetic controls or WT Akita mice. To optimize viewing of this image, please see the online version of this article at www.kidney-international.org.
