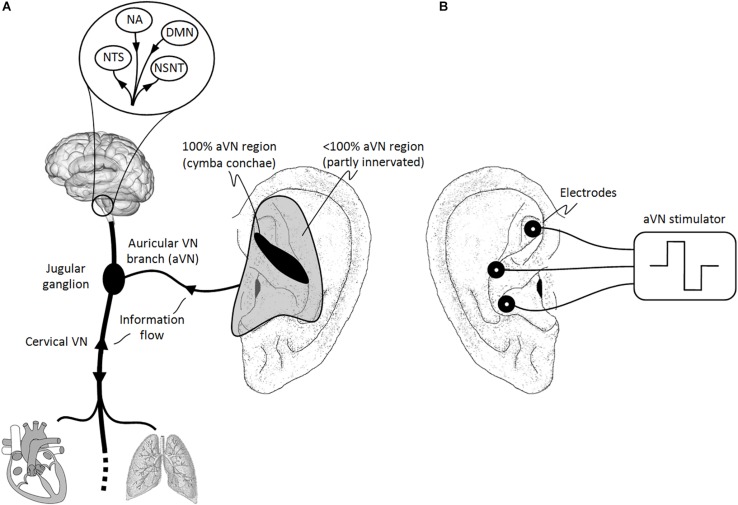
FIGURE 1.
Natural sensory innervation of the auricle versus its artificial stimulation. (A) The vagus nerve (VN) connects the brain with most of the organs within the thorax and abdomen. Afferent auricular branches (aVN) leave the cervical VN at the level of the jugular ganglion just outside the cranium and innervate the rather central regions of the pinna of the outer ear (Peuker and Filler, 2002). (B) Electric stimulation of aVN endings with needle electrodes located within these central regions. NTS, nucleus of the solitary tract; NSNT, nucleus spinalis of the trigeminal nerve; NA, nucleus ambiguous; DMN, dorsal motor nucleus. This figure and figure caption was originally published in the sister manuscript to this review (Kaniusas et al., 2019), which was published in Frontiers of Neuroscience under the creative commons attribution license CC BY 4.0.