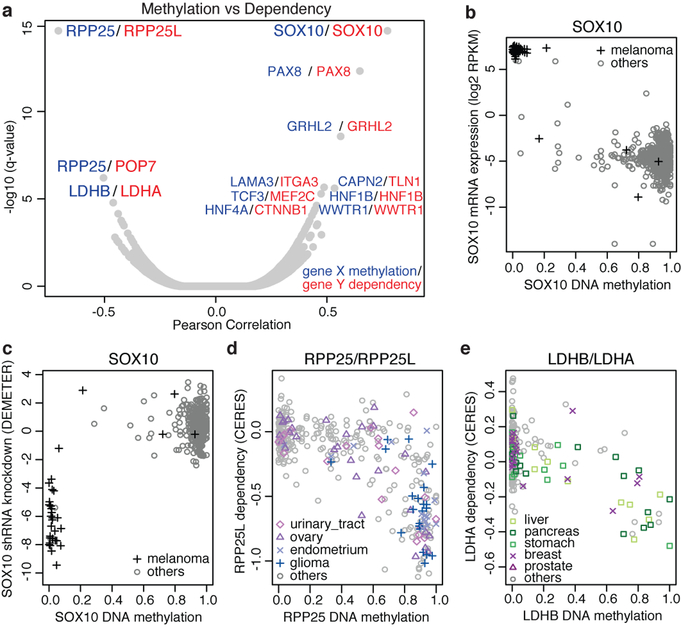
Fig. 2. DNA methylation and cancer dependence.
a, Global correlation between DNA methylation and gene dependency of the same gene or associated genes (StringDB). Top pairs (q < 5 × 10−5) are labelled (n = 45–380; Supplementary Table 8). b, c, Hypomethylation of SOX10 in melanoma cell lines is associated with SOX10 mRNA expression (Pearson’s r = −0.82, n = 824, P < 2.2 × 10−16) (b) and sensitivity to SOX10 knockdown (Pearson’s r = 0.79, n = 376, P < 2.2 × 10−16) (c). RPKM, reads per kilobase of transcript per million mapped reads. d, Promoter hypermethylation of RPP25 is a marker for vulnerability to RPP25L knockout (Pearson’s r = −0.71, n = 369, P < 2.2 × 10−16). e, LDHB methylation confers sensitization to LDHA knockout (Pearson’s r = −0.52, n = 362, P < 2.2 × 10−16).