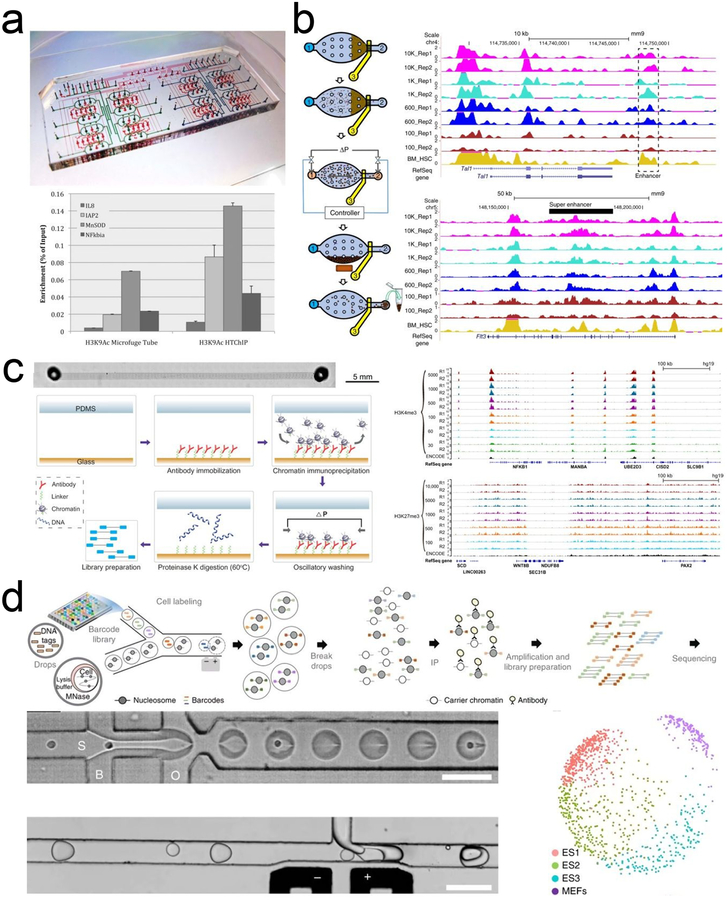
Figure 2 |. Microfluidic technologies for profiling histone modifications and transcription factor bindings.
a. HTChIP with reagent-containing flow channels (blue) and valve-actuating control channels (red). Reprinted with permission122. Copyright 2012 The Royal Society of Chemistry. b. MOWChIP-seq protocol, its performance on H3K4me3 and H3K27ac, and comparison with competing technologies. Reprinted with permission113. Copyright 2015 Macmillan Publishers Ltd. c. SurfaceChIP-seq (left panel) generated highly correlated data for H3K4me3 from 30–5000 GM12878 cells and for H3K27me3 from 100–10,000 cells (right panel). Reprinted with permission129. Copyright 2018 American Association for the Advancement of Science. d. Drop-ChIP procedure and multidimensional scaling plot showing three distinct ES cell subpopulations. Scale bars are 100 μm. Reprinted with permission110. Copyright 2015 Macmillan Publishers Ltd.