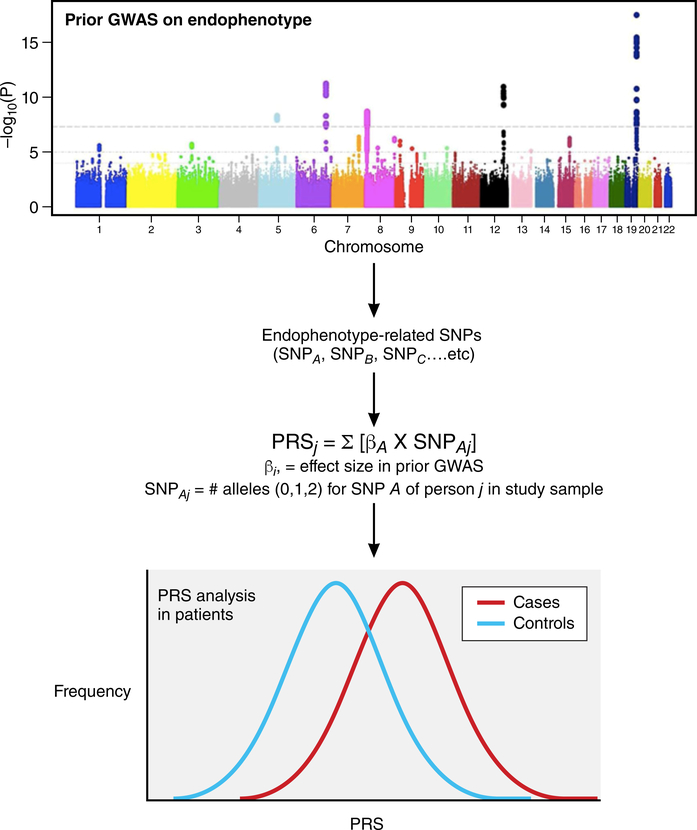
Figure 3:
Assessing the role of endophenotype-related single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in disease susceptibility and risk prediction. Large-scale genome-wide association studies (GWAS) identify endophenotype-related SNPs. Polygenic risk scores (PRS) are then calculated for cases and controls by summing the number of alleles weighted by the allele-specific effect size (β) for all endophenotype-related SNPs. The association of PRS with disease not only confirms a role for the endophenotype in question in disease susceptibility, but also contribute to the development of genetic risk predictors.