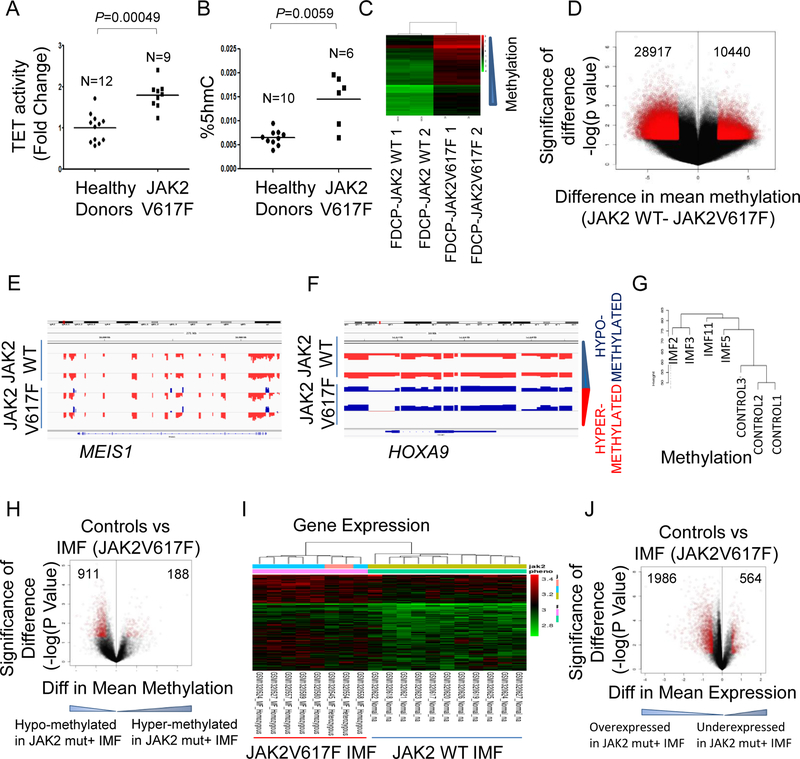
Fig. 6. JAK2V617F leads to increased 5-hmC and genome wide loss of cytosine methylation in primary patient samples.
(A, B) Constitutively active form of JAK2 (JAK2 V617F) in patients with myeloproliferative disorder polycythemia vera exhibit elevated levels of TET activity and 5-hmC content without impacting 5-mC levels. Primary CD34+ cells purified from patient samples or healthy donors were cultured for 6 days and basophilic erythroblasts generated from these patient samples was used to determine TET2 activity and 5-hmC contents. (C) FDCP cells were transfected with JAK2V617F and wildtype JAK2 and genome wide cytosine methylation was determined by the HELP assay. Unsupervised clustering revealed that samples with JAK2V617F mutation were epigenetically distinct and were characterized by more hypomethylated loci. (D) Differentially demethylated loci were significantly more than hypermethylated loci in JAK2V617F FDCP cells. (E, F) Integration with gene expression profiling done in same samples revealed that hypomethylation affecting gene promoters was associated with increased gene expression as shown for Meis1 and Hoxa9 genes. (G) Unsupervised clustering of methylation profiles generated by the HELP assay from 4 myelofibrosis patients with JAK2V617F mutation (without TET2 mutation) and 3 healthy controls shows that the controls are distinct from the JAK2+ cases. (H) Volcano plot shows 911 signficantly hypomethylated loci in JAK2 mutant samples as opposed to 188 hypermethylated loci. (I) Unsupervised clustering of gene expression profiles from 8 myelofibrosis patients with JAK2V617F mutation and 11 healthy controls shows distinct clustering. (J) Volcano plot shows 1986 overexpressed genes in JAK2 mutant samples as opposed to 564 under-expressed genes.