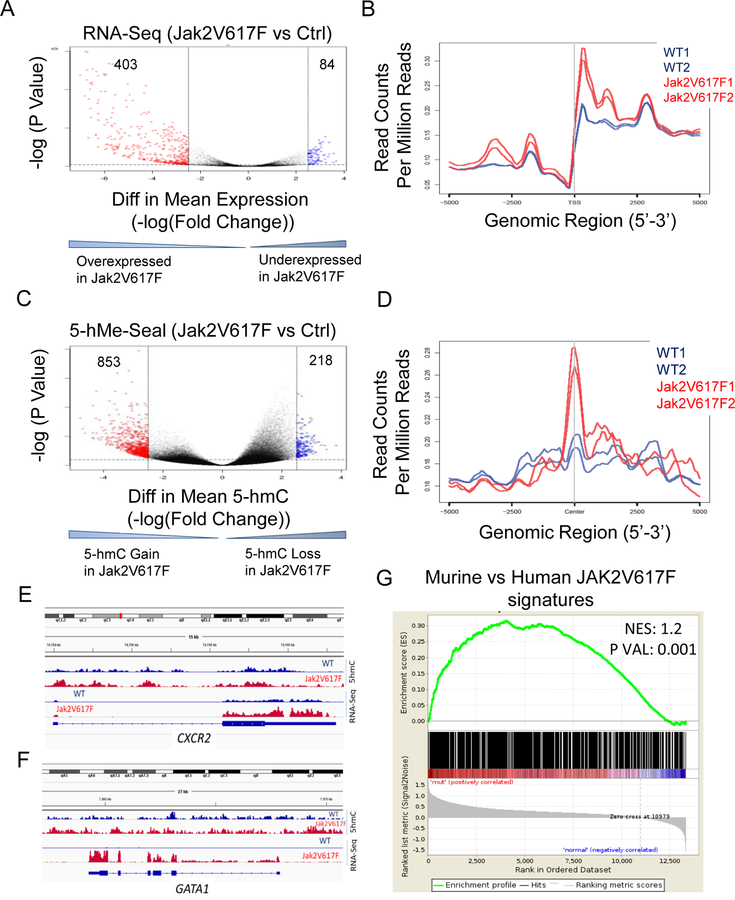
Fig. 7. JAK2V617F leads to 5-hmC gain in vivo that correlates with gene expression.
(A, B) Mice with transgenic expression of constitutively active form of Jak2 (Jak2V617F) and wild-type controls were used to isolate erythroid progenitor cells (sorted CD71+) from marrow and spleen. RNA-seq was performed and bioinformatics analysis revealed a greater numbers of differential expression of transcripts as well as overexpressed transcripts in Jak2V617F samples compared to the wild-type mice. (C) 5-hMe-Seal assay was performed for whole genome 5-hmC analysis, which revealed increased accumulation of 5-hmC peaks in Jak2V617F mice erythroid samples. Differential 5-hmC gain was calculated in 2 Jak2V617F and 2 WT mice. (D) A co-localization plot combining 5-hmc and gene expression was constructed showing the coverage of the RNA-seq samples within the regions defined by the 5-hmc peaks. Positive co-localization of expressed transcripts was seen around 5hmC peaks and this was more pronounced in Jak2V617F samples. (E, F) Plots showing increased expression of Gata1 and Cxcr2 in Jak2V617F samples with increased gain of 5-hmC at their promoters in Jak2V617F samples is seen. (G) Differential 5-hmC regions in Jak2V617F samples were correlated with differentially expressed genes in human Jak2V617F samples. A positive correlation was seen between murine and human on GSEA.