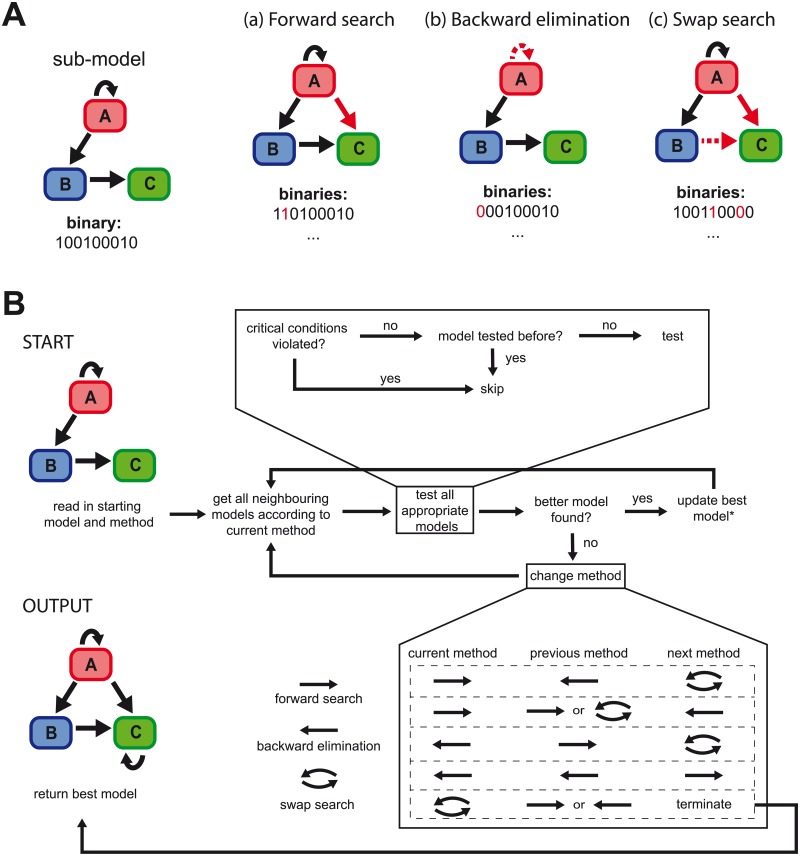
Fig 2. Outline of the algorithm.
(A) Based on a given (sub-)model of the global model, FAMoS works by creating and testing neighbouring models against experimental data. Thereby, the algorithm distinguishes between three main methods for exploring the model space including (a) forward search, in which a parameter that was not considered in the previous model is additionally considered, (b) backward elimination, in which a parameter of the current model is deleted from the analysis, and (c) swap search, in which two parameters out of pre-defined parameter sets are exchanged. (B) Starting with a pre-defined model and method, FAMoS creates the neighbouring models and compares their ability to describe the experimental data, with the methods and/or models dynamically updated at the end of each iteration. The algorithm finally returns the model that was found to best explain the experimental data.