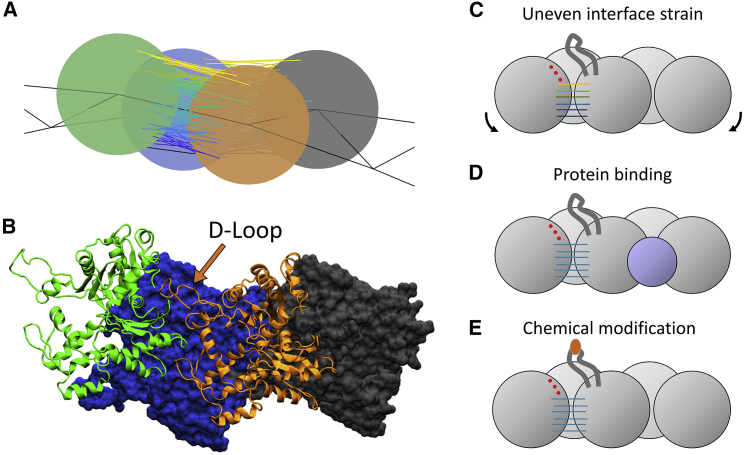
Figure 7.
Strain localization predicts the importance of the D-loop for bare-actin-filament bending rupture. (A) A snapshot is given of the most strained longitudinal interfaces of a compressed actin filament and (B) the corresponding structure of the actin filament (PDB: 2ZWH) oriented with the pointed end to the left. The highest strain in bent filaments is between subdomain 2 and subdomain 1 of the adjacent monomers. This region spatially corresponds to the location of the D-loop. Interface disruption can be caused by (C) uneven application of force on an interface; (D) protein (cofilin) binding, leading to a structural change; or (E) chemical modification of amino acids (as by MICAL). To see this figure in color, go online.