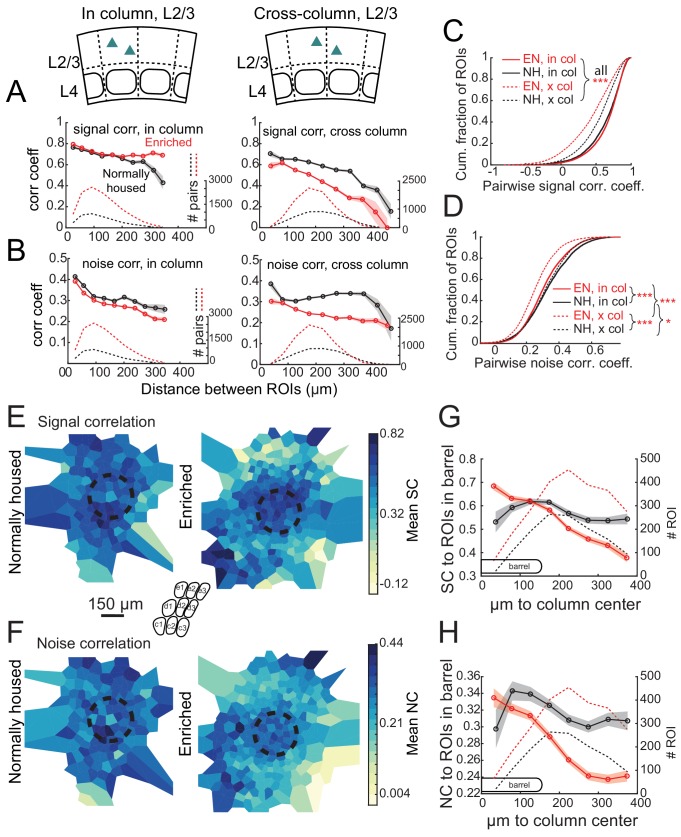
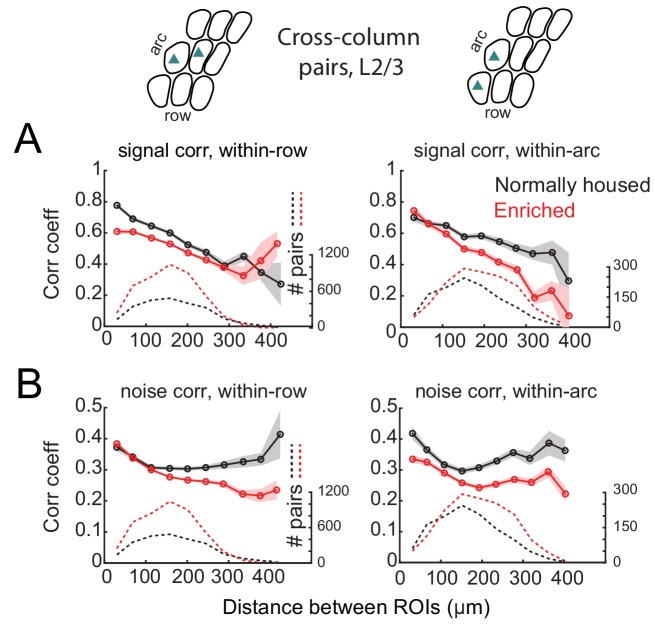
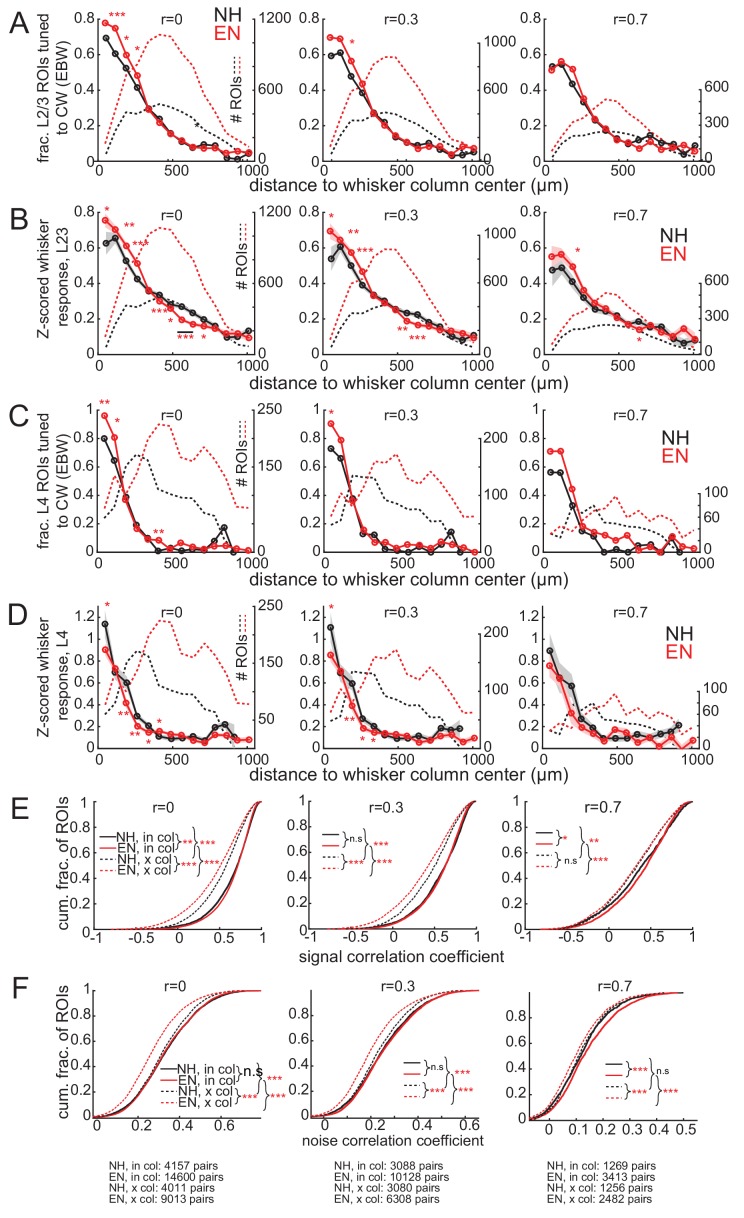
Figure 5. Enrichment alters the spatial structure of signal and noise correlations in L2/3.
(A) Mean signal correlation across responsive L2/3 cell pairs as a function of inter-ROI distance, for cell pairs within a column (left) or across columns (right). Shaded regions denote SEM. Dashed, number of cell pairs in each bin. Insets show schematic of cell locations. (B) Mean noise correlation across all responsive L2/3 pairs, plotted as in (A). (C–D) Cumulative distribution of signal correlation (C) or noise correlation (D) for all within-column (in-col) and across-column (x-col) pairs. Asterisks denote difference between distributions computed by ANOVA with multiple comparisons correction. (E) Spatial map of mean signal correlation for sample ROIs within a position bin to all ROIs located within a reference whisker column. For each sample ROI, the mean signal correlation to all ROIs within the reference column was calculated. Sample ROIs were then clustered into spatial bins, and the mean signal correlation for each bin was plotted. The dashed circle is the reference column (shown as an average barrel diameter around the column center). (F) Spatial map of mean noise correlation to all ROIs within the reference whisker column, shown as in (E). (G) Mean signal correlation from sample ROIs to all cells in a reference column, as a function of sample ROI distance from column center. Shading is SEM. (H) Same as for (G), but for noise correlations. G-H show that enrichment steepens correlation gradients at column edges.