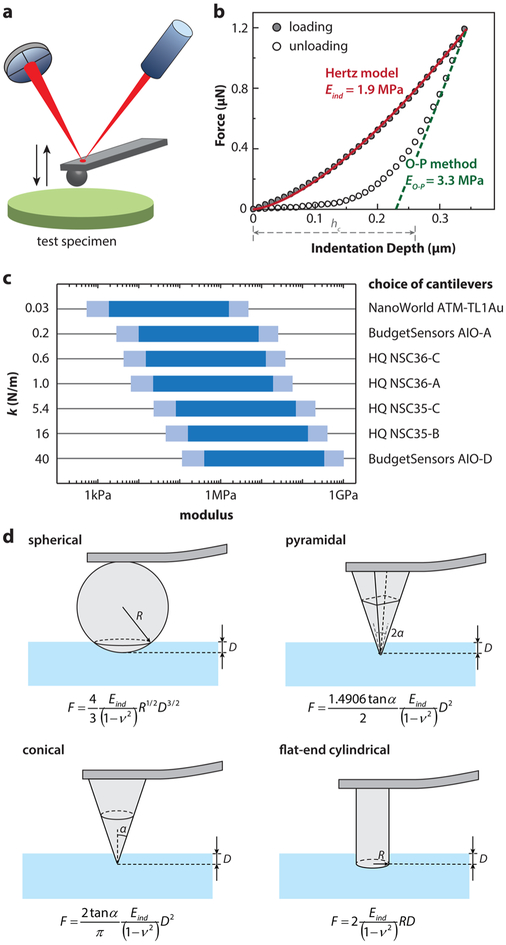
Figure 2.
AFM-nanoindentation of cartilage and soft tissues. (a) Schematic of AFM-based nanoindentation. (b) Representative nanoindentation curve on adult wild-type murine cartilage and corresponding data analysis at 10 μm/s displacement rate with a microspherical tip (R ≈ 5 μm) in PBS. Indentation moduli were calculated by fitting with (1) the Hertz model on the entire loading curve and (2) the Oliver–Pharr method on the top 25% of the unloading curve (punch parameter ε = 0.75, hc denotes the corresponding contact depth). Both fits yield R2 > 0.99. (c) Suitable choices of cantilever spring constants for specimens with different orders of elastic moduli. (d) Schematics of commonly used contact geometries and contact mechanics models for AFM-based nanoindentation: spherical, pyramidal, conical, and flatend indenter tips.67