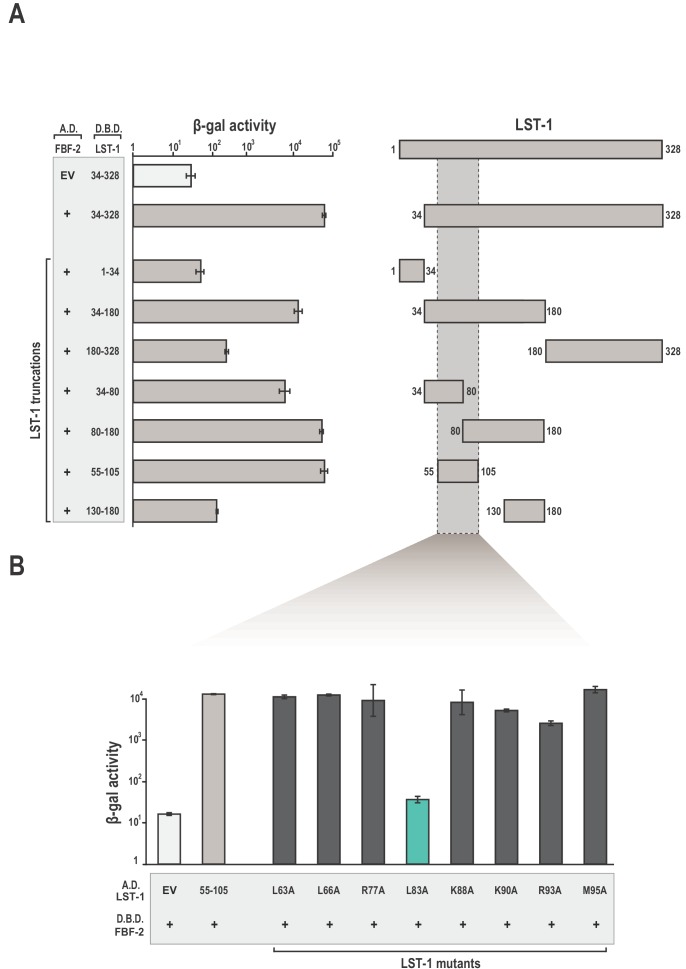
Figure 1. Identification of a minimal fragment of LST-1 that interacts with FBF-2.
(A) Yeast 2-hybrid analyses of interaction between the FBF-2 PUM domain fused to a GAL4 activation domain (A.D.) and LST-1 fragments fused to the LexA DNA-binding domain (D.B.D.). A negative control empty vector (EV) with no FBF-2 fused to the activation domain and a positive control with the FBF-2 PUM domain fused to the activation domain were assessed with LST-1 34–328 fused to the DNA-binding domain and are shown at the top of the graph. (B) LST-1 L83 is critical for interaction with FBF-2. Yeast 2-hybrid analyses were conducted with LST-1 residues 55–105 fused to a GAL4 activation domain and the PUM domain of FBF-2 fused to the LexA DNA-binding domain. Mutants in LST-1 that interfered with FBF-2 interaction are colored green and those that were competent for interaction are colored gray. Binding activity is shown as units of β-galactosidase (β-gal) activity normalized to cell count. Error bars indicate the standard deviation of three biological replicate measurements. A schematic representation of the yeast 2-hybrid assay is illustrated in Figure 1—figure supplement 1 and results of yeast 2-hybrid analyses of LST-1 and FBF homologs are shown in Figure 1—figure supplement 2.
Figure 1—figure supplement 1. A schematic of the yeast two-hybrid assay.
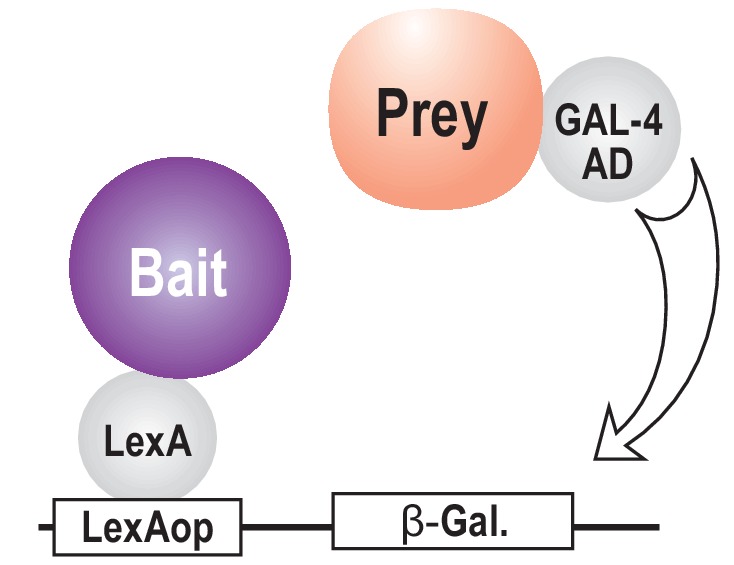
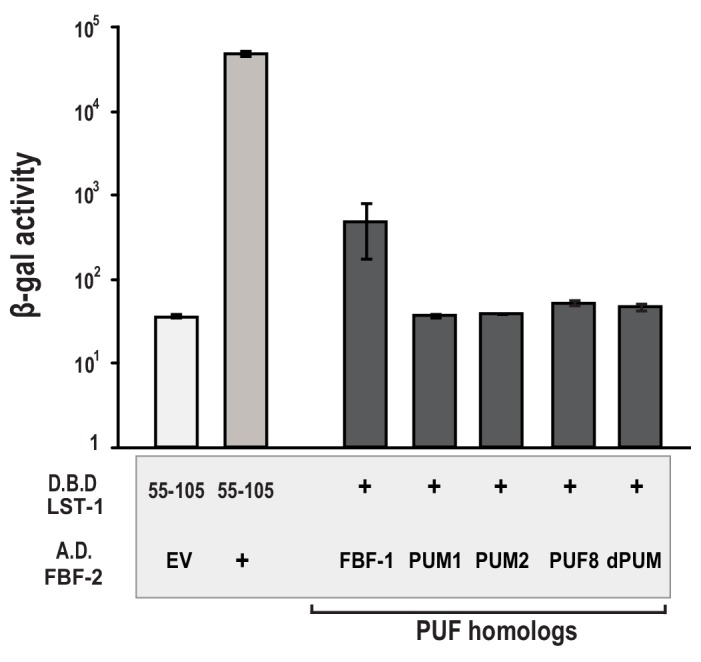
Figure 1—figure supplement 2. LST-1 interacts with FBF but not homologous PUF proteins.