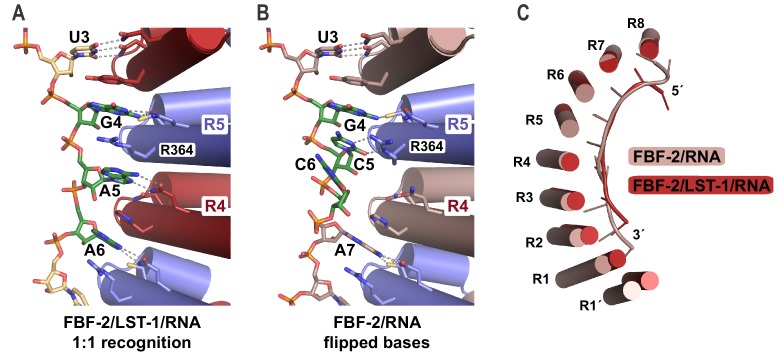
Figure 4. FBF-2 in the ternary complex binds to RNA using a 1:1 recognition mode and its curvature is more pronounced.
(A) FBF-2 recognizes the central nucleotides in a compact RNA using repeats 4 and 5. The crystal structure of the FBF-2/LST-1/RNA ternary complex is shown with FBF-2 displayed as a ribbon diagram with cylindrical helices. PUM repeats are colored alternately red and blue. RNA recognition side chains from each PUM repeat are shown with dotted lines indicating interactions with the RNA bases. Central nucleotides 4–6 (green) within a compact RNA element (beige) are shown as stick representations colored by atom type (red, oxygen; blue, nitrogen; orange, phosphorus). Electron density for the compact RNA nucleotides 4–6 is shown in Figure 4—figure supplement 1. (B) FBF-2 binds to directly stacked and flipped central nucleotides in the extended gld-1 RNA motif. The crystal structure of the FBF-2/gld-1 RNA binary complex (PDB ID 3V74) is shown as a ribbon diagram with cylindrical helices. Central nucleotides 4–6 (green) within the gld-1 RNA (mauve) are shown as stick models. (C) Superposition of FBF-2 within ternary and binary complexes reveals increased curvature in the FBF-2/LST-1/RNA ternary complex. RNA-binding helices and RNA cartoons are shown for FBF-2 in the binary (mauve) and ternary (red) complexes.
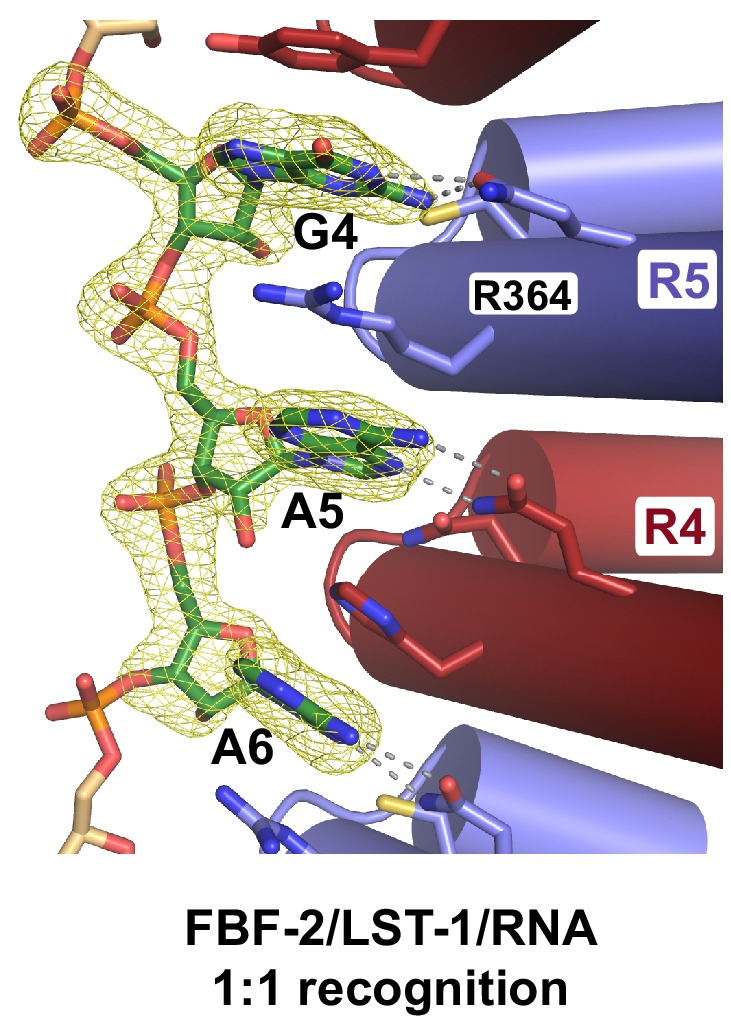
Figure 4—figure supplement 1. Fo-Fc simulated annealing omit map for the cFBE RNA nucleotides 4–6, contoured at 3 σ.