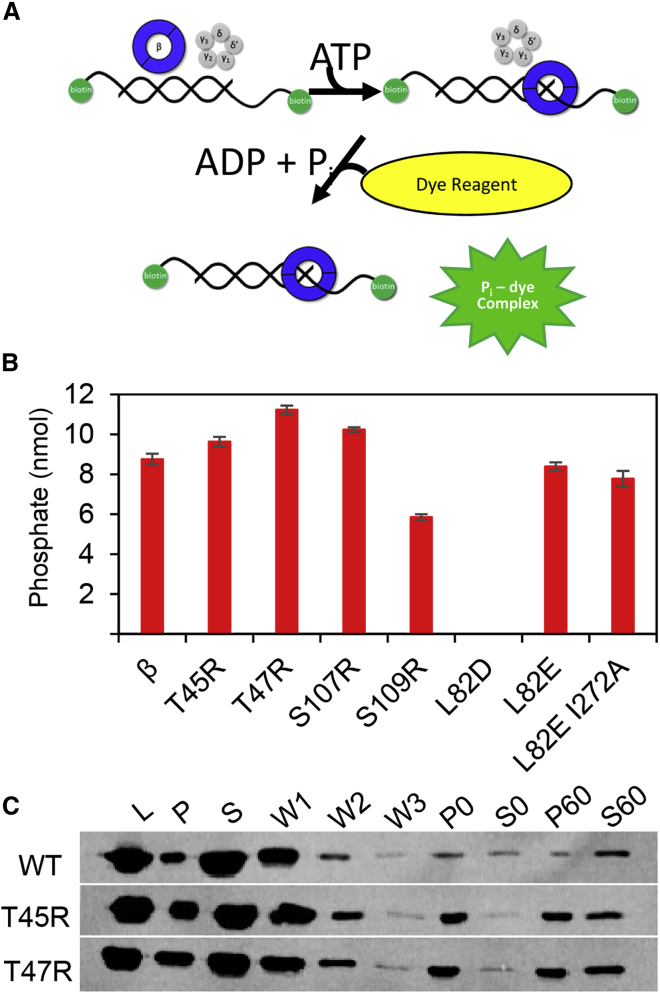
Figure 5.
ATPase activity of the γ-complex measured using a BIOMOL Green colorimetric reagent. (A) A schematic depicting loading of the β-clamp onto a primer-template DNA with biotinylated 5′-ends. The template is longer than the primer, resulting in a 3′ recessed end onto which the γ-complex loads β in the presence of ATP. ATP hydrolysis ejects the clamp loader. The increase of inorganic phosphate following the loading reaction is measured by addition of the BIOMOL Green reagent. (B) A bar graph showing the amount of phosphate released (nmol) during the loading reaction after the intrinsic γ-complex ATPase activity is subtracted (γ-complex hydrolyzes ATP in the presence of DNA, β enhances the ATPase activity of the γ-complex). Average nmol of phosphate released and standard deviations from at least three replicates are reported. (C) Immunoblot detection of β loaded onto a primer-template substrate using a bead-based assay for WT β and the variants indicated. Input control (L) indicates the amount of β in each loading reaction. After three wash steps (W1, W2, and W3), pellet (P) fractions indicate loaded β and supernatant (S) fractions indicate unloaded β, respectively, for both 0- and 60-min time points (also see Fig. S3)