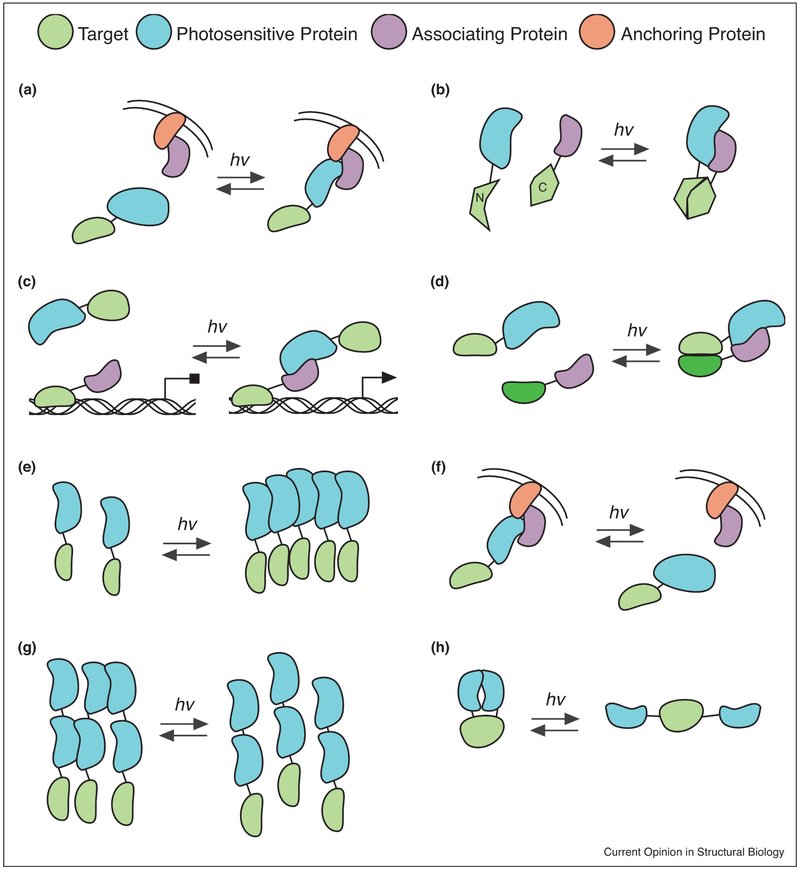
Figure 2. Photodimerizer approaches to regulate protein function.
Schematic showing approaches used to regulate protein activity using photodimerizers. The target protein regulated is colored in green, with photosensory proteins in blue, partner proteins in purple, and anchoring proteins in orange. A) Recruitment to anchored subcellular location. One of the photodimerizer components is fused to a protein or peptide allowing anchored subcellular localization (plasma membrane is shown as an example), while the other is fused to a target protein of interest. Light illumination allows recruitment of the target to the anchored location. B) Reconstitution of a split protein. Activity is achieved by fusing the N-terminus and C-terminus of a split protein to the interacting photodimerizers, allowing functional reconstitution with light. C) Reconstitution of a split transcription factor. Variation of (B), where one of the photodimerizer partners is fused to a DNA binding domain, where it can bind to DNA at a promoter site. The partner photodimerizer is fused to a transcriptional activation domain. Light allows recruitment of the activation domain, resulting in activation of transcription. D) Dimerization of two different proteins. Photodimerizers can be used to bring two different (or the same) target proteins together with light. E) Oligomerization. A target is fused to a photoreceptor (such as CRY2) that undergoes light dependent oligomerization, which can be used to induce or disrupt activity. F) Sequestration/release. A target protein is anchored (sequestered) at an inactive subcellular location, then released with light illumination to allow function. G) Dissociation of protein clusters. Used with light-dissociated dimerizers, protein assembles into clusters that impede trafficking or activity, which are dissociated/dissolved with light. H) Single chain caging. Interacting partners are presented on the same protein chain, along with a target protein or domain. Function of the target protein is sterically or allosterically impeded when photodimerizers are bound, but enabled when partners dissociate.