Figure 2. Effects of wogonoside on VEGF secretion, protein and mRNA expression and transcriptional activity in MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-468 cell lines.
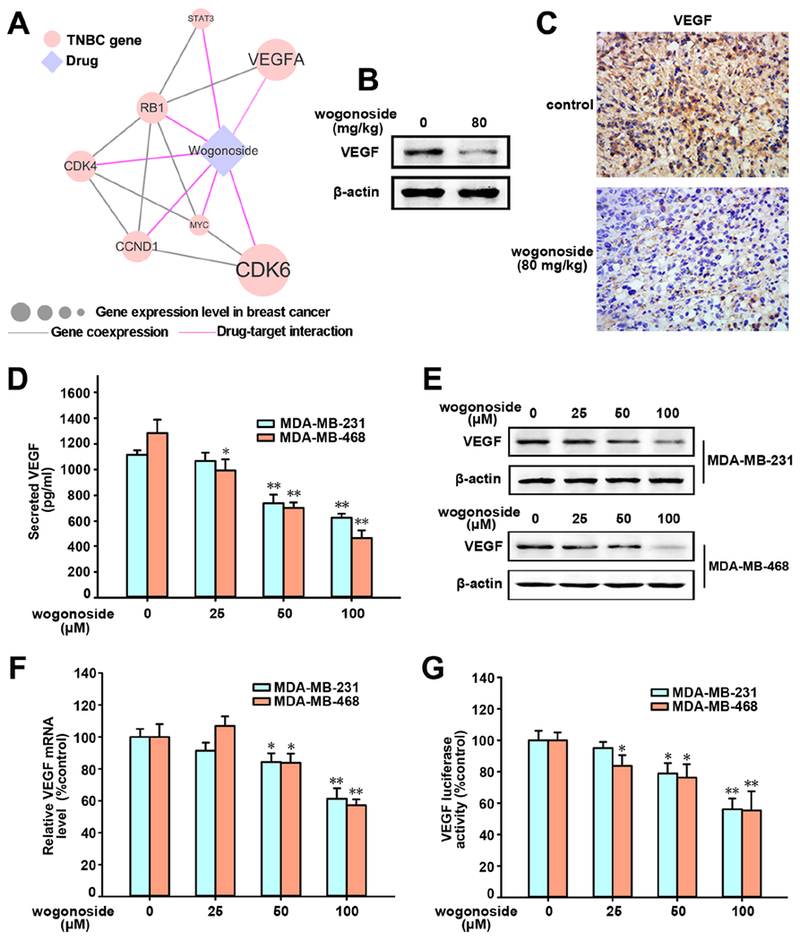
(A) Network analysis highlighting the inferred mechanism-of-action for wogonoside in TNBC. The potential molecular mechanisms of wogonoside against TNBC were investigated via integration of known drug targets and experimentally validated TNBC genes into tissue-specific co-expressed protein-protein interactome network (see Methods). Node size indicates the protein-coding gene expression level in breast comparing to other 31 tissues from GTEx database (Consortium, 2015). Larger size highlighting the high expression level in breast comparing to other tissues. Co-expression denotes the co-expressed gene pairs (p-value < 0.05, F-statistics) encoding protein-protein interactions in TNBC RNA sequencing data from The Cancer Genome Atlas database (Cancer Genome Atlas, 2012). (B) Effect of wogonoside on VEGF expression in xenograft model of MDA-MB-231 cells in nude mice (n=5) was detected by Western blot analysis. (C) The expression of VEGF in xenograft model was detected by immunochemistry using specific antibody. (D) The concentration of VEGF in MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-468 CM were measured by ELISA kits. (E) VEGF expression was detected by western blot analysis using specific antibodies. (F) The mRNA level of VEGF was investigated by RT-PCR. (G) VEGF transcriptional activity was tested by Dual-Luciferase reporter assay. The comparisons were made relative to the control group and the significance of the difference is indicated as *P value < 0.05 and **P value < 0.01. See also Figures S1 and S4.
