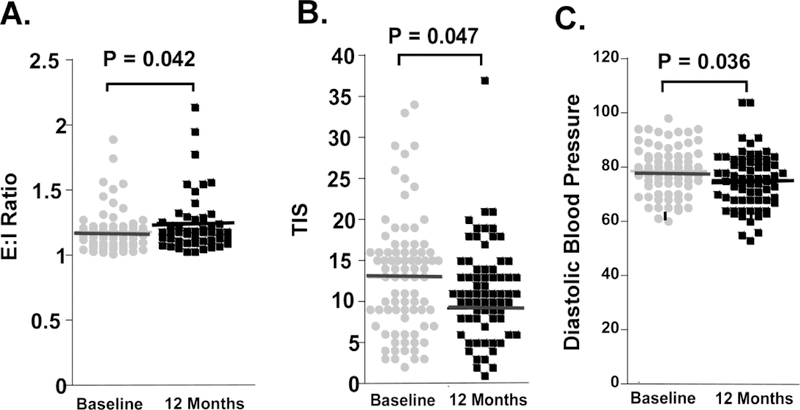
Figure 3. Improvement in measures of autonomic function in subjects with neuropathy and impaired glucose tolerance or type 2 diabetes mellitus receiving “standard of care” dietary and exercise counselling over a 12 month period.
The protocol was performed prospectively, was masked, and standardized. “Standard of care” advice included recommendations to undertake aerobic exercise for 150 minutes/week, up to 30 minutes per session, and a goal of reducing baseline weight by 7 percent. However, none of the recommendations were enforced or monitored. The technician performing the outcome measures was masked to the patient intervention.
(A) Increased expiration:inspiration (E:I ratio, n = 50) after 1 year (P=0.042). Base 95% CI:1.14, 1.22. 1 year 95% CI: 1.20, 1.44.
(B) Decreased Total Impact Score (TIS) on the Survey of Autonomic Symptoms (SAS, n = 71),
(C) Decreased resting diastolic blood pressure (n = 72).