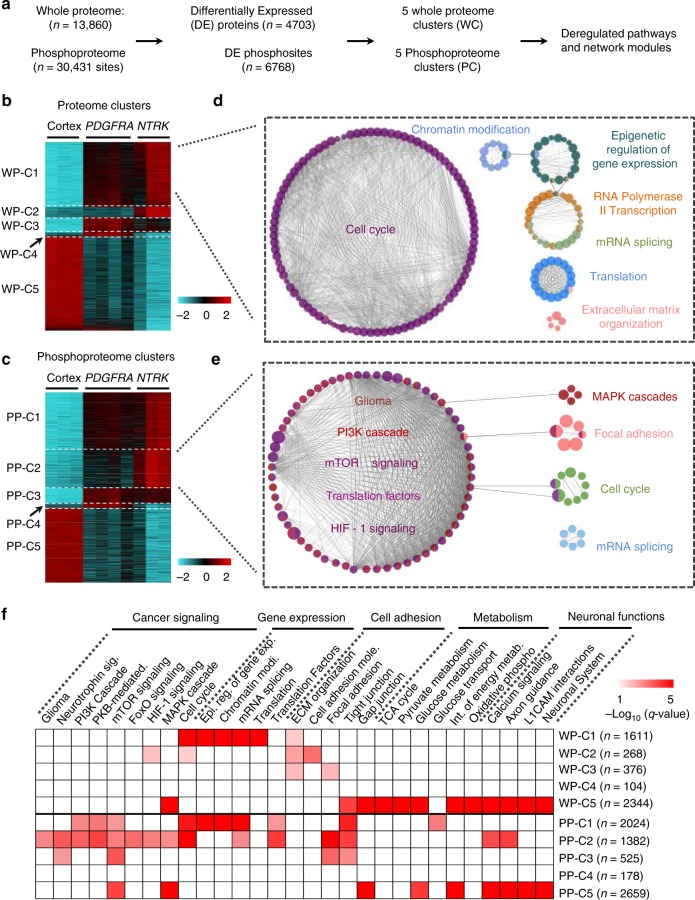
Fig. 3.
Global network analyses identify both canonical and novel network modules in HGGs. a Overview of the analysis strategy. Differential expression (DE) genes were selected through one-way ANOVA and clustered by WGCNA. Each coexpression cluster was utilized for pathway and network module analysis with ClueGO. b, c Multiple DE whole protein (WP) and phosphoprotein (PP) coexpression clusters with distinct patterns were detected through WGCNA analysis. Heatmaps show the z-scores of log-transformed DE WPs or PPs. WP-C whole proteome cluster, PP-C phosphoproteome cluster. The color keys present the Z scores of proteins. d, e Interconnected network modules identified in some clusters (e.g. WP-C1 and PP-C2). DE proteins/phosphorylations in WP-C1 and PP-C2 were first applied for pathway enrichment, enriched pathways were then applied for pathway to pathway network analysis. Network modules are shown in circular layout nodes and are represented by distinct colors; nodes with more than one color indicate that proteins detected in these specific pathway nodes are shared by more than one network module. Each node represents a pathway, with node size reflecting pathway enrichment significance, p value was generated by Fisher’s exact test, and cutoff 0.05 was applied for pathway enrichment. Functionally related pathways are connected by edges and then grouped to network modules. f Summary of pathways enriched in the coexpression clusters. Representative pathways detected in each cluster were organized based on biological processes. Chart shows the significance of each enriched pathway, the significance is reflected by −Log10 (q value). Fisher’s exact test was performed to obtain p values, and further adjusted by Benjamini−Hochberg procedure to generate q values. Cutoff of q value 0.05 was applied. Number of DE proteins, phosphorylations was shown on the right side of each cluster. HGG high-grade glioma