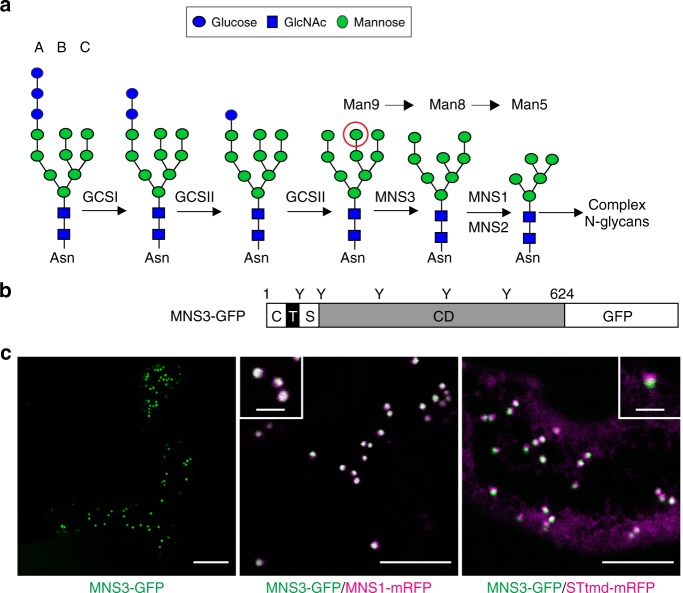
Fig. 1.
Arabidopsis MNS3 is a Golgi-resident protein. a The early steps of N-glycan processing in A. thaliana are shown. The three branches of the N-linked Glc3Man9GlcNAc2 oligosaccharide precursor are marked A, B, and C. The red circle indicates the terminal α1,2-linked mannose residue that is cleaved off by MNS3 from the B-branch. GCSI: α-glucosidase I; GCSII: α-glucosidase II; MNS3: ER-α-mannosidase I; MNS1/MNS2: Golgi-α-mannosidase I. b Illustration of the domain organization of MNS3. C, cytoplasmic tail (41 aa); T, predicted transmembrane domain (26 aa); S, stem region (42 aa); CD, catalytic domain (515 aa). Positions of putative N-glycosylation sites are indicated (Y). The depicted numbers represent the length of the protein (624 amino acids). c Subcellular localization of MNS3. Confocal images show N. benthamiana leaf epidermal cells transiently expressing MNS3-GFP (green) alone (scale bar = 20 µm) and in combination with the cis/medial-Golgi protein MNS1-mRFP (magenta, scale bar = 5 µm) or the medial/trans-Golgi marker STtmd-mRFP (magenta, scale bar = 5 µm). The insets show a higher magnification of individual dual-colored Golgi stacks (scale bar = 2 µm). Images were acquired 2 days post infiltration (dpi)