Fig. 9.
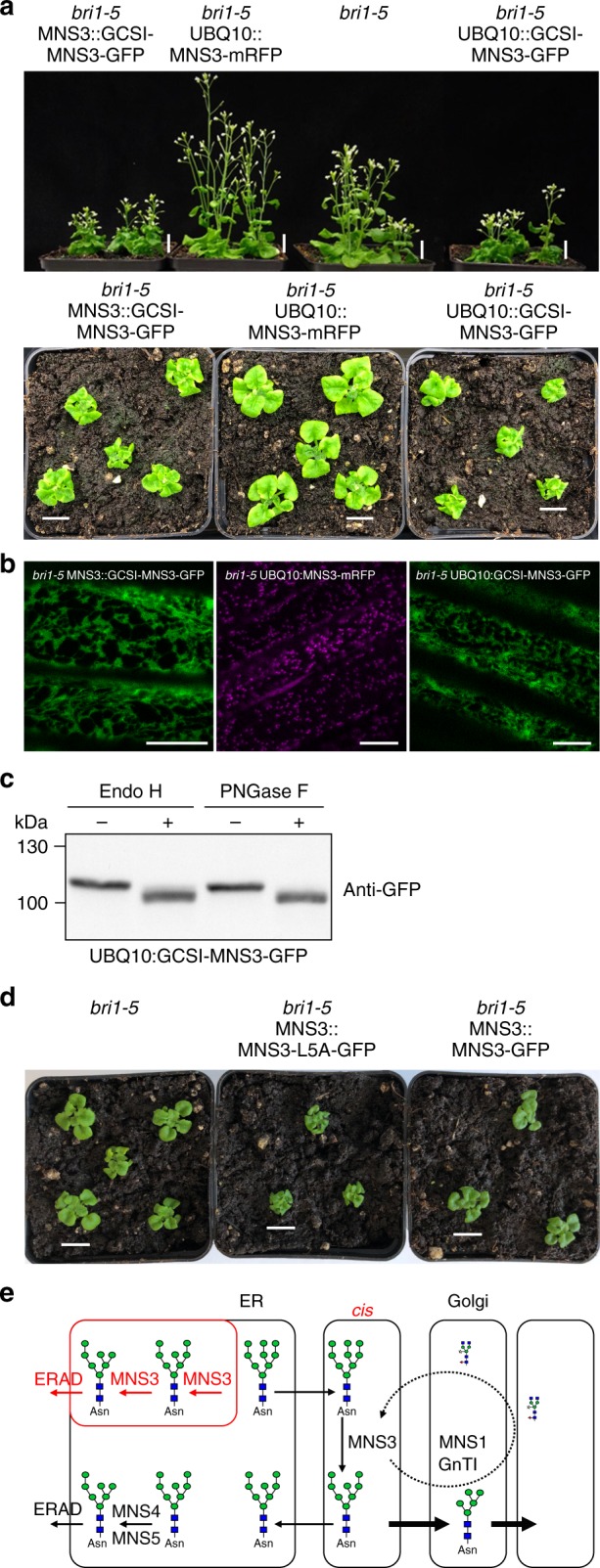
ER retention of MNS3 enhances the bri1-5 phenotype. a Phenotype of Arabidopsis bri1-5 and transgenic bri1-5 plants expressing either MNS3::GCSI-MNS3-GFP, UBQ10::MNS3-mRFP, or UBQ10::GCSI-MNS3-GFP. Images of 5-week-old (upper panel) or 26-day-old (lower panel) soil-grown plants are shown. Scale bars = 1 cm. b Confocal images of transgenic bri1-5 plants expressing either MNS3::GCSI-MNS3-GFP (green), UBQ10::MNS3-mRFP (magenta), or UBQ10::GCSI-MNS3-GFP (green). Scale bar = 15 µm. c Crude protein extracts from leaves of N. benthamiana wildtype plants transiently expressing UBQ10::GCSI-MNS3-GFP were subjected to Endo H and PNGase F digestion. Proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and blots were probed with anti-GFP antibodies. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. d Phenotype of bri1-5 and transgenic bri1-5 plants expressing either MNS3::MNS3-L5A-GFP or MNS3::MNS3-GFP. Images of 22-day-old soil-grown plants are shown. Scale bars = 1 cm. e Proposed model for MNS3-catalyzed mannose trimming as part of regular N-glycan processing of glycoproteins in the Golgi or in the ER leading to enhanced ERAD. In the regular N-glycan processing pathway, ER-processed glycoproteins travel to the cis-Golgi, where they are modified by MNS3. Secretory proteins are further processed by Golgi-resident enzymes starting with MNS1 and GnTI, whereas ER-resident glycoproteins are cycled back to their home destination. MNS3-processed ERAD substrates are similarly returned to the ER, where they are subjected to demannosylation by MNS4/MNS5 generating the N-glycan signal triggering glycoprotein ERAD in plants. The presence of MNS3 in the ER promotes the generation of the glycan signal for degradation either by interacting with other ER-resident ERAD factors like MNS4/MNS5 and modulation of their activity toward enhanced degradation of misfolded proteins or by contributing directly to the generation of the exposed α1,6-linked mannose on the C-branch
