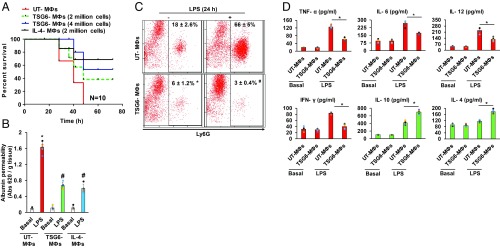
Fig. 4.
Adoptive transfer of TSG6-primed MФs via i.t. instillation suppresses LPS-induced lung injury. (A) Age- and weight-matched mice were challenged with a lethal dose of LPS (20 mg/kg i.p.) and i.t.-instilled with indicated number of TSG6- or IL-4–stimulated or unstimulated BMMФs. Mortality was monitored for 72 h. The mice instilled with TSG6- or IL-4–stimulated BMMФs (TSG6 MФs and IL-4 MФs) showed markedly increased survival compared with the unstimulated BMMФs (UT-MФs) group. *P < 0.05 vs. UT MФs group; n = 10 per group. (B) Lung vascular permeability (uptake of EBA) was assessed in LPS-challenged (10 mg/kg i.p.) mice concurrently instilled with UT or TSG6- or IL-4–stimulated MФs. The mice instilled with TSG6- or IL-4–treated MФs showed significantly reduced lung vascular permeability; n = 6 mice per group. *P < 0.05 vs. UT MФs group. (C) Ly6G population was measured by flow cytometric analysis in BALF of mice i.t.-instilled with either UT- or TSG6-treated BMMФs, and challenged with i.p. LPS (10 mg/kg) for 24 h. (D) BALF concentrations of proinflammatory (TNF-α, IL-6, IL-12, and IFN-γ) and antiinflammatory (IL-10 and IL-4) cytokines measured with ELISA. *P < 0.05 vs. UT MФs group.