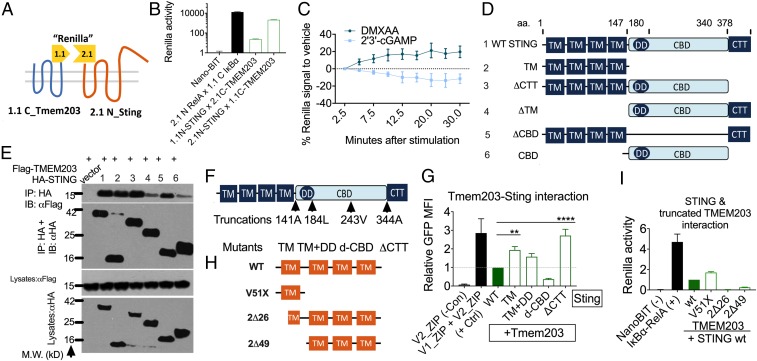
Fig. 5.
Molecular determinants of TMEM203-STING complex formation. (A) Detection of TMEM203-STING interaction by Renilla PCA. Tmem203 was tagged at its C terminus with the 1.1 (small) fragment of Renilla luciferase reporter while Sting was tagged at its N terminus with the 2.1 (large) Renilla fragment. (B) TMEM203 and STING interact in live cells. HEK293 T cells were cotransfected with the indicated fusion protein expression vectors; Renilla luciferase signal was detected by Nano-Glo live cell luciferase assay. Relative luminescence intensity was plotted compared with the negative control transfection of Nano-BIT construct. n = 3. (C) TMEM203-STING interaction is differentially regulated by DMXAA and 2′3′-cGAMP. TMEM203 and STING were tagged at their N termini with the 1.1 and 2.1 fragment of Renilla luciferase, respectively, to test for a molecular interaction between these proteins in live cells. Tmem203 and Sting were transfected into HEK293 T cells for 24 h and were then stimulated with DMXAA (50 µg/mL) and 2′3′-cGAMP (10 µg/mL) for the indicated time. Luciferase activity was calculated relative to Hoechst fluorescence (cell numbers) and calculated relative to the 2.5-min time point. n = 4. (D and E) TMEM203 coprecipitates with the STING N-terminal transmembrane region. WT and five mutant Sting constructs were created as indicated and fused with HA tags. CBD, CBD domain of Sting; ΔCBD, Sting without cyclic-dinucleotide binding domain (CBD); ΔCTT, Sting without cytoplasmic tail; ΔTM, Sting without transmembrane domain; TM, transmembrane domain. (E) HEK293 T cells were transfected with either empty vector, Flag-Tmem203, or HA-Sting (WT/mutants). Tmem203-containing complexes were immunoprecipitated (IP) using anti-Flag–coated beads and blotted for Flag and HA, as indicated. Lysates were also immunoblotted (IB) for Flag and HA. n = 2. (F) STING truncation mutants. Four serial truncation Sting mutants were individually created: after its N-terminal transmembrane domains (TM); after the dimerization domain (TM+DD); inside the cyclic dinucleotide binding domain (d-CBD); and before the C-terminal cytoplasmic terminal tail (ΔCTT). (G) TMEM203-STING association is not eliminated by C-terminal truncations of STING. HEK293 T cells were cotransfected with the Tmem203 and Sting WT/mutants cloned into the Venus vector system as described in Fig. 2E; Venus fluorescence signal was detected by flow cytometry. Relative mean fluorescence intensity was plotted compared with the STING WT–TMEM203 interaction. n = 4 to 7. (H) TMEM203 truncation mutants. Three mutants, expressing truncated versions of TMEM203 have been generated, as indicated. (I) AA1-51 of TMEM203 are sufficient to interact with STING. HEK293 T cells were cotransfected with the Tmem203 WT/mutants and Sting cloned into the Renilla reporter system as described in Fig. 5A. Renilla activity was measured 24 h posttransfection, and relative luciferase activity was calculated relative to Hoechst fluorescence (cell numbers). n = 3. **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001.